Characterization of Oxygen Nanobubbles and In Vitro Evaluation of Retinal Cells in Hypoxia
- PMID: 36763051
- PMCID: PMC9927786
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.12.2.16
Characterization of Oxygen Nanobubbles and In Vitro Evaluation of Retinal Cells in Hypoxia
Abstract
Purpose: Vein or artery occlusion causes a hypoxic environment by preventing oxygen delivery and diffusion to tissues. Diseases such as retinal vein occlusion, central retinal artery occlusion, or diabetic retinopathy create a stroke-type condition that leads to functional blindness in the effected eye. We aim to develop an oxygen delivery system consisting of oxygen nanobubbles (ONBs) that can mitigate retinal ischemia during a severe hypoxic event such as central retinal artery occlusion.
Methods: ONBs were synthesized to encapsulate oxygen saturated molecular medical grade water. Stability, oxygen release, biocompatibility, reactive oxygen species, superoxide, MTT, and terminal uridine nick-end labeling assays were performed. Cell viability was evaluated, and safety experiments were conducted in rabbits.
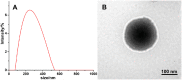
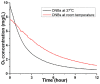
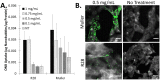
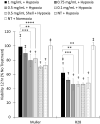
Results: The ONBs were approximately 220 nm in diameter, with a zeta potential of -58.8 mV. Oxygen release studies indicated that 74.06 µg of O2 is released from the ONBs after 12 hours at 37°C. Cell studies indicated that ONBs are safe and cells are viable. There was no significant increase in reactive oxygen species, superoxide, or double-stranded DNA damage after ONB treatment. ONBs preserve mitochondrial function and viability. Histological sections from rabbit eyes indicated that ONBs were not toxic.
Conclusions: The ONBs proposed have excellent oxygen holding and release properties to mitigate ischemic conditions in the retina. They are sterile, stable, and nontoxic.
Translation relevance: ONB technology was evaluated for its physical properties, oxygen release, sterility, stability, and safety. Our results indicate that ONBs could be a viable treatment approach to mitigate hypoxia during ischemic conditions in the eye upon timely administration.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures




Similar articles
-
Oxygen Nanobubbles-Embedded Hydrogel as Wound Dressing to Accelerate Healing.ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2023 Jul 17;6(14):13116-13126. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.3c01812. eCollection 2023 Jul 28. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2023. PMID: 37533542 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering oxygen nanobubbles for the effective reversal of hypoxia.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup3):S318-S327. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2018.1492420. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30032670
-
Hypoxia-Responsive Oxygen Nanobubbles for Tissues-Targeted Delivery in Developing Tooth Germs.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 15;9:626224. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.626224. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33659251 Free PMC article.
-
Retinal oxygen distribution. Its role in the physiopathology of vasoproliferative microangiopathies.Retina. 1995;15(4):332-47. Retina. 1995. PMID: 8545580 Review.
-
Retinal oximetry and systemic arterial oxygen levels.Acta Ophthalmol. 2018 Nov;96 Suppl A113:1-44. doi: 10.1111/aos.13932. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 30460761 Review.
Cited by
-
NanoBubble-Mediated Oxygenation: Elucidating the Underlying Molecular Mechanisms in Hypoxia and Mitochondrial-Related Pathologies.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Nov 30;13(23):3060. doi: 10.3390/nano13233060. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38063756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogel-Based Oxygen and Drug Delivery Dressing for Improved Wound Healing.ACS Omega. 2024 May 22;9(22):24095-24104. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c03324. eCollection 2024 Jun 4. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38854553 Free PMC article.
-
Addressing retinal hypoxia: pathophysiology, therapeutic innovations, and future prospects.Ther Adv Ophthalmol. 2024 Sep 26;16:25158414241280187. doi: 10.1177/25158414241280187. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39376745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic delivery of oxygen using artificial oxygen carriers demonstrates the possibility of treating a wide range of diseases.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Jan 18;23(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-03060-9. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 39827150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxygen Nanobubbles-Embedded Hydrogel as Wound Dressing to Accelerate Healing.ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2023 Jul 17;6(14):13116-13126. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.3c01812. eCollection 2023 Jul 28. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2023. PMID: 37533542 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

