Accuracy of linear-probe ultrasonography in diagnosis of infraorbital rim fractures
- PMID: 36763227
- PMCID: PMC9918656
- DOI: 10.1186/s13089-022-00298-y
Accuracy of linear-probe ultrasonography in diagnosis of infraorbital rim fractures
Abstract
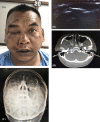
Background: Maxillofacial fractures are a common cause of visits to emergency department, accounting for more than 400,000 annual visits in the United States. Gold standard diagnostic tool is conventional computerized tomography (CT) or 3DCT reconstruction. However, the disadvantages of CT are radiation exposure, unavailable in some hospital and expensiveness. Whereas the bony structures overlap is a problem in diagnostic when using plain film X-ray. The objective of this study is to show the accuracy of a linear-probe ultrasound compared to computed tomography and plain film X-ray in diagnosis of infraorbital rim fracture.
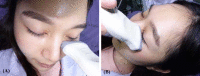
Methods: Patients clinically suspected of an inferior orbital rim fracture underwent linear-probe ultrasonographic investigation, plain film X-ray and CT. CT was used as gold standard in this diagnostic study. A radiologist and senior resident of plastic surgery were the examiner and interobserver for comparison.
Result: A total of 34 patients with suspected infraorbital rim fractures were investigated. Sensitivity of the linear-probe ultrasonography versus CT in the detection of infraorbital rim fracture was 92.9% (95% CI 66.1-99.8), specificity was 90.0% (95% CI 68.3-98.8), positive predictive value was 86.7% (95% CI 59.5-98.3), negative predictive value was 94.7% ( 95% CI 74.0-99.9), accuracy 91%.
Conclusion: Linear probe ultrasonography is a good diagnostic tool and has better reliability than the plain film X-ray and can be used as alternative to CT in inferior orbital rim fracture.
Keywords: Computerized tomography; Infraorbital rim fracture; Linear probe ultrasonography.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ultrasound versus computed tomography in the imaging of orbital floor fractures.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004 Feb;62(2):150-4. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2003.01.004. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004. PMID: 14762746 Clinical Trial.
-
The diagnostic value of ultrasonography in the detection of orbital floor fractures with a curved array transducer.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004 Jan;33(1):13-8. doi: 10.1054/ijom.2003.0456. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004. PMID: 14690654 Clinical Trial.
-
[Interobserver variation of the sonographic diagnosis of orbital floor fractures and fractures of the infraorbital margin].Mund Kiefer Gesichtschir. 2004 Nov;8(6):337-43. doi: 10.1007/s10006-004-0571-7. Epub 2004 Oct 21. Mund Kiefer Gesichtschir. 2004. PMID: 15503239 German.
-
Diagnostic Performance of Plain Film, Ultrasonography, and Computed Tomography in Nasal Bone Fractures: A Systematic Review.Plast Surg (Oakv). 2018 Nov;26(4):286-292. doi: 10.1177/2292550317749535. Epub 2018 Jan 9. Plast Surg (Oakv). 2018. PMID: 30450348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adult scaphoid fracture.Acad Emerg Med. 2014 Feb;21(2):101-21. doi: 10.1111/acem.12317. Acad Emerg Med. 2014. PMID: 24673666
Cited by
-
[The use of fracture sonography in midface traumatology].HNO. 2025 Feb;73(2):152-162. doi: 10.1007/s00106-024-01541-9. Epub 2024 Dec 16. HNO. 2025. PMID: 39680107 Review. German.
-
Intraoperative ultrasonographic evaluation of inferior orbital rim reduction in non-comminuted zygomatic fractures: A case series of six patients.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2025 Sep;134:111771. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2025.111771. Epub 2025 Aug 5. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40782456 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
