Nanomaterial-based biohybrid hydrogel in bioelectronics
- PMID: 36763293
- PMCID: PMC9918666
- DOI: 10.1186/s40580-023-00357-7
Nanomaterial-based biohybrid hydrogel in bioelectronics
Abstract
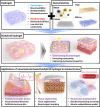
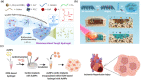
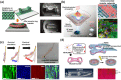
Despite the broadly applicable potential in the bioelectronics, organic/inorganic material-based bioelectronics have some limitations such as hard stiffness and low biocompatibility. To overcome these limitations, hydrogels capable of bridging the interface and connecting biological materials and electronics have been investigated for development of hydrogel bioelectronics. Although hydrogel bioelectronics have shown unique properties including flexibility and biocompatibility, there are still limitations in developing novel hydrogel bioelectronics using only hydrogels such as their low electrical conductivity and structural stability. As an alternative solution to address these issues, studies on the development of biohybrid hydrogels that incorporating nanomaterials into the hydrogels have been conducted for bioelectronic applications. Nanomaterials complement the shortcomings of hydrogels for bioelectronic applications, and provide new functionality in biohybrid hydrogel bioelectronics. In this review, we provide the recent studies on biohybrid hydrogels and their bioelectronic applications. Firstly, representative nanomaterials and hydrogels constituting biohybrid hydrogels are provided, and next, applications of biohybrid hydrogels in bioelectronics categorized in flexible/wearable bioelectronic devices, tissue engineering, and biorobotics are discussed with recent studies. In conclusion, we strongly believe that this review provides the latest knowledge and strategies on hydrogel bioelectronics through the combination of nanomaterials and hydrogels, and direction of future hydrogel bioelectronics.
Keywords: Bioelectronics; Biohybrid hydrogel; Biorobotics; Flexible devices; Nanomaterial.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Multifunctional Conductive Hydrogel Interface for Bioelectronic Recording and Stimulation.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Sep;13(22):e2400562. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202400562. Epub 2024 Jun 6. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 38773929 Review.
-
Tissue adhesive hydrogel bioelectronics.J Mater Chem B. 2021 Jun 2;9(22):4423-4443. doi: 10.1039/d1tb00523e. J Mater Chem B. 2021. PMID: 33908586 Review.
-
Hydrogel Bioelectronics for Health Monitoring.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Aug 14;13(8):815. doi: 10.3390/bios13080815. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37622901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogel-Based Bioelectronics and Their Applications in Health Monitoring.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 30;13(7):696. doi: 10.3390/bios13070696. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37504095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Degradable and Recyclable Hydrogels for Sustainable Bioelectronics.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Jul 3;16(26):32887-32905. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c05663. Epub 2024 Jun 21. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38904545 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioaugmented design and functional evaluation of low damage implantable array electrodes.Bioact Mater. 2025 Jan 8;47:18-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.12.033. eCollection 2025 May. Bioact Mater. 2025. PMID: 39872211 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced WBG power semiconductor packaging: nanomaterials and nanotechnologies for high-performance die attach paste.Nano Converg. 2025 Jul 23;12(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s40580-025-00503-3. Nano Converg. 2025. PMID: 40699507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mussel-inspired resilient hydrogels with strong skin adhesion and high-sensitivity for wearable device.Nano Converg. 2024 Mar 21;11(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s40580-024-00419-4. Nano Converg. 2024. PMID: 38512587 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances of Stretchable Nanomaterial-Based Hydrogels for Wearable Sensors and Electrophysiological Signals Monitoring.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Aug 27;14(17):1398. doi: 10.3390/nano14171398. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39269060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrochemical Wearable Biosensors and Bioelectronic Devices Based on Hydrogels: Mechanical Properties and Electrochemical Behavior.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Aug 15;13(8):823. doi: 10.3390/bios13080823. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37622909 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
