Expression, purification, and characterisation of the p53 binding domain of Retinoblastoma binding protein 6 (RBBP6)
- PMID: 36763571
- PMCID: PMC9916574
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277478
Expression, purification, and characterisation of the p53 binding domain of Retinoblastoma binding protein 6 (RBBP6)
Abstract
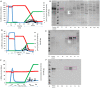
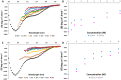
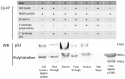
RBBP6 is a 250 kDa eukaryotic protein known to be a negative regulator of p53 and essential for embryonic development. Furthermore, RBBP6 is a critical element in carcinogenesis and has been identified as a potential biomarker for certain cancers. RBBP6's ability to interact with p53 and cause its degradation makes it a potential drug target in cancer therapy. Therefore, a better understating of the p53 binding domain of RBBP6 is needed. This study presents a three-part purification protocol for the polyhistidine-tagged p53 binding domain of RBBP6, expressed in Escherichia coli bacterial cells. The purified recombinant domain was shown to have structure and is functional as it could bind endogenous p53. We characterized it using clear native PAGE and far-UV CD and found that it exists in a single form, most likely monomer. We predict that its secondary structure is predominantly random coil with 19% alpha-helices, 9% beta-strand and 14% turns. When we exposed the recombinant domain to increasing temperature or known denaturants, our investigation suggested that the domain undergoes relatively small structural changes, especially with increased temperature. Moreover, we notice a high percentage recovery after returning the domain close to starting conditions. The outcome of this study is a pure, stable, and functional recombinant RBBP6-p53BD that is primarily intrinsically disordered.
Copyright: © 2023 Russell, Ntwasa. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

