Women experiencing homelessness and mental illness in a Housing First multi-site trial: Looking beyond housing to social outcomes and well-being
- PMID: 36763583
- PMCID: PMC9916643
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277074
Women experiencing homelessness and mental illness in a Housing First multi-site trial: Looking beyond housing to social outcomes and well-being
Abstract
Objective: There is scant research on the effectiveness of permanent supportive housing for homeless women with mental illness. This study examines the effectiveness of Housing First with an unprecedentedly large sample of homeless women from five Canadian cities, and explore baseline risk factors that predict social, health and well-being outcomes over a 24 month-period.
Methods: The At Home/Chez Soi multi-site randomized controlled Housing First trial recruited over 600 women between October 2009 and July 2011. This is a post-hoc subgroup exploratory analysis of self-identified women with at least one follow-up interview who were randomized to Housing First (HF) (n = 374) or treatment-as-usual (TAU) (n = 279) and had at least one follow-up interview. Linear mixed models and generalized estimating equations were used after multiple imputation was applied to address missing data.
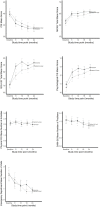
Results: At the end of follow-up, the mean percentage of days spent stably housed was higher for women in the intervention 74.8% (95%CI = 71.7%-77.8%) compared with women in the treatment-as-usual group, 37.9% (95%CI = 34.4%-41.3%), p<0.001. With few exceptions, social and mental health outcomes were similar for both groups at 6-, 12-, 18- and 24-months post-enrollment. Suicidality was a consistent predictor of increased mental health symptoms (beta = 2.85, 95% CI 1.59-4.11, p<0.001), decreased quality of life (beta = -3.99, 95% CI -6.49 to -1.49, p<0.001), decreased community functioning (beta = -1.16, 95% CI -2.10 to -0.22, p = 0.015) and more emergency department visits (rate ratio = 1.44, 95% CI 1.10-1.87, p<0.001) over the study period. Lower education was a predictor of lower community functioning (beta = -1.32, 95% CI -2.27 to -0.37, p = 0.006) and higher substance use problems (rate ratio = 1.27, 95% CI 1.06-1.52, p = 0.009) during the study.
Conclusions: Housing First interventions ensured that women experiencing homelessness are quickly and consistently stably housed. However, they did not differentially impact health and social measures compared to treatment as usual. Ensuring positive health and social outcomes may require greater supports at enrolment for subgroups such as those with low educational attainment, and additional attention to severity of baseline mental health challenges, such as suicidality.
Trial registration: International Standard Randomized Control Trial Number Register Identifier: ISRCTN42520374.
Copyright: © 2023 O'Campo et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Gaetz S, Dej E, Richter T, Redman M. The State of Homelessness in Canada 2016. Toronto: 2016.
-
- Employment and Social Development Canada. Everyone Counts 2018: Highlights—Preliminary results from the second nationally coordinated Point-in-Time count of homelessness in Canadian communities. 2019.
-
- Schwan K, Versteegh A, Perri M, Caplan R, Baig K, Dej E, et al.. The State of Women’s Housing Need & Homelessness in Canada: A Literature Review. Hache A., Nelson A., Kratochvil E., & Malenfant J. (Eds). Toronto, ON: Canadian Observatory on Homelessness Press. 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

