Na, K-ATPase α1 cooperates with its endogenous ligand to reprogram immune microenvironment of lung carcinoma and promotes immune escape
- PMID: 36763655
- PMCID: PMC9916986
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ade5393
Na, K-ATPase α1 cooperates with its endogenous ligand to reprogram immune microenvironment of lung carcinoma and promotes immune escape
Abstract
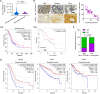
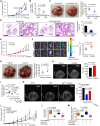
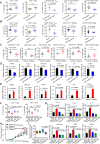
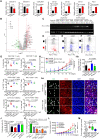
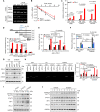
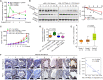
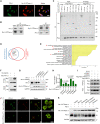
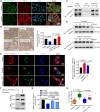
Dysregulated endocrine hormones (EHs) contribute to tumorigenesis, but how EHs affect the tumor immune microenvironment (TIM) and the immunotherapy of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is still unclear. Here, endogenous ouabain (EO), an adrenergic hormone, is elevated in patients with NSCLC and closely related to tumor pathological stage, metastasis, and survival. EO promotes the suppression of TIM in vivo by modulating the expression of immune checkpoint proteins, in which programmed cell death protein ligand 1 (PD-L1) plays a major role. EO increases PD-L1 transcription; however, the EO receptor Na- and K-dependent adenosine triphosphatase (Na, K-ATPase) α1 interacts with PD-L1 to trigger the endocytic degradation of PD-L1. This seemingly contradictory result led us to discover the mechanism whereby EO cooperates with Na, K-ATPase α1 to finely control PD-L1 expression and dampen tumoral immunity. In conclusion, the Na, K-ATPase α1/EO signaling facilitates immune escape in lung cancer, and manipulation of this signaling shows great promise in improving immunotherapy for lung adenocarcinoma.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Triple blockade of Ido-1, PD-L1 and MEK as a potential therapeutic strategy in NSCLC.J Transl Med. 2022 Nov 22;20(1):541. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03730-y. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36419183 Free PMC article.
-
B7-1 and programmed cell death-ligand 1 in primary and lymph node metastasis lesions of non-small cell lung carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2022 Jan;11(2):479-491. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4444. Epub 2021 Dec 14. Cancer Med. 2022. PMID: 34907653 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidation of the relationships of MET protein expression and gene copy number status with PD-L1 expression and the immune microenvironment in non-small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2020 Mar;141:21-31. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.01.005. Epub 2020 Jan 7. Lung Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31931443
-
Programmed death-ligand 1 expression in non-small cell lung carcinoma - mechanism of regulation, association with other markers, and therapeutic implication.Klin Onkol. 2022 Fall;35(5):372-376. doi: 10.48095/ccko2022372. Klin Onkol. 2022. PMID: 36443097 Review. English.
-
[Advances of PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway in immune escape and treatment for non-small cell lung cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2014 Oct 20;17(10):734-40. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2014.10.05. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25342040 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
ORC6 acts as an effective prognostic predictor for non‑small cell lung cancer and is closely associated with tumor progression.Oncol Lett. 2024 Jan 11;27(3):96. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14229. eCollection 2024 Mar. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38288041 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Compounds Inhibit the Growth of W12 Cervical Precancer Cells Containing Episomal or Integrant HPV DNA; Tanshinone IIA Synergizes with Curcumin in Cervical Cancer Cells.Viruses. 2024 Dec 31;17(1):55. doi: 10.3390/v17010055. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39861845 Free PMC article.
-
ATP1A1-Driven Intercellular Contact Between Dental Pulp Stem Cell and Endothelial Cell Enhances Vasculogenic Activity.Int Dent J. 2025 Jul 7;75(5):100870. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2025.100870. Online ahead of print. Int Dent J. 2025. PMID: 40628202 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling ammonia-induced cell death: a new frontier in clear cell renal cell carcinoma prognosis.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 31;16:1636977. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1636977. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40821775 Free PMC article.
-
Sensational site: the sodium pump ouabain-binding site and its ligands.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Apr 1;326(4):C1120-C1177. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00273.2023. Epub 2024 Jan 15. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38223926 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- J. M. Pitt, M. Vetizou, R. Daillere, M. P. Roberti, T. Yamazaki, B. Routy, P. Lepage, I. G. Boneca, M. Chamaillard, G. Kroemer, L. Zitvogel, Resistance mechanisms to immune-checkpoint blockade in cancer: Tumor-intrinsic and -extrinsic factors. Immunity 44, 1255–1269 (2016). - PubMed
-
- R. S. Herbst, D. Morgensztern, C. Boshoff, The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 553, 446–454 (2018). - PubMed
-
- M. J. Grant, R. S. Herbst, S. B. Goldberg, Selecting the optimal immunotherapy regimen in driver-negative metastatic NSCLC. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 18, 625–644 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

