Targeting HER3 for cancer treatment: a new horizon for an old target
- PMID: 36764093
- PMCID: PMC9929675
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2023.100790
Targeting HER3 for cancer treatment: a new horizon for an old target
Abstract
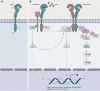
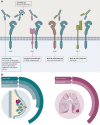
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 3 (HER3) is a member of the human epidermal growth factor receptors family, having as its main ligands neuregulins 1 and 2. Although its poor tyrosine kinase activity entails a weak oncogenic power on its own, HER3 can heterodimerize with HER2 and/or epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), leading to a drastic enhancement of transphosphorylation and activation of downstream signaling pathways, ultimately promoting oncogenesis, metastatic dissemination, and drug resistance. Given its ubiquitous expression across solid tumors, multiple efforts have been done to therapeutically target HER3 by blocking either the ligand binding domain or its dimerization with other receptors. Treatment with anti-HER3 monoclonal antibodies or bispecific antibodies, both as single agents and in combination with other compounds, unfortunately led to unsatisfactory results across several tumor types. The HER3-directed delivery of cytotoxic payloads through antibody-drug conjugates has recently demonstrated encouraging activity in several tumor types, however, suggesting a potential role for the therapeutic targeting of HER3 in cancer treatment.
Keywords: ADCs; HER3; breast cancer; lung cancer; patritumab deruxtecan.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HER3: Toward the Prognostic Significance, Therapeutic Potential, Current Challenges, and Future Therapeutics in Different Types of Cancer.Cells. 2023 Oct 25;12(21):2517. doi: 10.3390/cells12212517. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37947595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging importance of HER3 in tumorigenesis and cancer therapy.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2025 May;22(5):348-370. doi: 10.1038/s41571-025-01008-y. Epub 2025 Mar 14. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40087402 Review.
-
ERBB3 (HER3) is a key sensor in the regulation of ERBB-mediated signaling in both low and high ERBB2 (HER2) expressing cancer cells.Cancer Med. 2012 Aug;1(1):28-38. doi: 10.1002/cam4.10. Epub 2012 Jul 15. Cancer Med. 2012. PMID: 23342251 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of the HER2/HER3 signaling axis overcomes ligand-mediated resistance to trastuzumab in HER2-positive breast cancer.Cancer Med. 2019 Mar;8(3):1258-1268. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1995. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 30701699 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering multivalent antibodies to target heregulin-induced HER3 signaling in breast cancer cells.MAbs. 2014 Mar-Apr;6(2):340-53. doi: 10.4161/mabs.27658. Epub 2013 Dec 26. MAbs. 2014. PMID: 24492289 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Antitumor activity of PAbs generated by immunization with a novel HER3-targeting protein-based vaccine candidate in preclinical models.Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 16;14:1472607. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1472607. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39479017 Free PMC article.
-
HER3 is widely expressed across diverse subtypes of NSCLC in a retrospective analysis of archived tissue samples.Future Oncol. 2024;20(37):2961-2970. doi: 10.1080/14796694.2024.2398983. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Future Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39320886 Free PMC article.
-
A prospective study of HER3 expression pre and post neoadjuvant therapy of different breast cancer subtypes: implications for HER3 imaging therapy guidance.Breast Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 29;26(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s13058-024-01859-w. Breast Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38951909 Free PMC article.
-
SIBP-03, a novel anti-HER3 antibody, exerts antitumor effects and synergizes with EGFR- and HER2-targeted drugs.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Apr;45(4):857-866. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01221-4. Epub 2024 Jan 10. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 38200149 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting HER3 to overcome EGFR TKI resistance in NSCLC.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 4;14:1332057. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1332057. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38239350 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hynes N.E., MacDonald G. ErbB receptors and signaling pathways in cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009;21(2):177–184. - PubMed
-
- Burgess A.W., Cho H.-S., Eigenbrot C., et al. An open-and-shut case? recent insights into the activation of EGF/ErbB receptors. Mol Cell. 2003;12(3):541–552. - PubMed
-
- Montero J.C., Rodríguez-Barrueco R., Ocaña A., Díaz-Rodríguez E., Esparís-Ogando A., Pandiella A. Neuregulins and cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(11):3237–3241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

