Impact of Copy Number Variants and Polygenic Risk Scores on Psychopathology in the UK Biobank
- PMID: 36764568
- PMCID: PMC10409883
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2023.01.028
Impact of Copy Number Variants and Polygenic Risk Scores on Psychopathology in the UK Biobank
Abstract
Background: Our understanding of the impact of copy number variants (CNVs) on psychopathology and their joint influence with polygenic risk scores (PRSs) remains limited.
Methods: The UK Biobank recruited 502,534 individuals ages 37 to 73 years living in the United Kingdom between 2006 and 2010. After quality control, genotype data from 459,855 individuals were available for CNV calling. A total of 61 commonly studied recurrent neuropsychiatric CNVs were selected for analyses and examined individually and in aggregate (any CNV, deletion, or duplication). CNV risk scores were used to quantify intolerance of CNVs to haploinsufficiency. Major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder PRSs were generated for White British individuals (N = 408,870). Mood/anxiety factor scores were generated using item-level questionnaire data (N = 501,289).
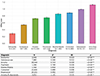
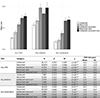
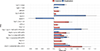
Results: CNV carriers showed higher mood/anxiety scores than noncarriers, with the largest effects seen for intolerant deletions. A total of 11 individual deletions and 8 duplications were associated with higher mood/anxiety. Carriers of the 9p24.3 (DMRT1) duplication showed lower mood/anxiety. Associations remained significant for most CNVs when excluding individuals with psychiatric diagnoses. Nominally significant CNV × PRS interactions provided preliminary evidence that associations between select individual CNVs, but not CNVs in aggregate, and mood/anxiety may be modulated by PRSs.
Conclusions: CNVs associated with risk for psychiatric disorders showed small to large effects on dimensional mood/anxiety scores in a general population cohort, even when excluding individuals with psychiatric diagnoses. CNV × PRS interactions showed that associations between select CNVs and mood/anxiety may be modulated by PRSs.
Keywords: Anxiety; Copy number variants; Depression; Mood; Polygenic risk scores; Psychopathology.
Copyright © 2023 Society of Biological Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
All authors reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
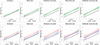
Similar articles
-
Association of Rare Copy Number Variants With Risk of Depression.JAMA Psychiatry. 2019 Aug 1;76(8):818-825. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.0566. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30994872 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Characterization of Copy Number Variants Associated With Neurodevelopmental Disorders in a Large-scale Multiancestry Biobank.JAMA Psychiatry. 2022 Mar 1;79(3):250-259. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.4080. JAMA Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35080590 Free PMC article.
-
Genotype-phenotype associations in children with copy number variants associated with high neuropsychiatric risk in the UK (IMAGINE-ID): a case-control cohort study.Lancet Psychiatry. 2019 Jun;6(6):493-505. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(19)30123-3. Epub 2019 May 2. Lancet Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31056457
-
The contribution of copy number variants to psychiatric symptoms and cognitive ability.Mol Psychiatry. 2023 Apr;28(4):1480-1493. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-01978-4. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Mol Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36737482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of copy number variations on brain structure and risk for psychiatric illness: Large-scale studies from the ENIGMA working groups on CNVs.Hum Brain Mapp. 2022 Jan;43(1):300-328. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25354. Epub 2021 Feb 21. Hum Brain Mapp. 2022. PMID: 33615640 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Contributions of common and rare genetic variation to different measures of mood and anxiety disorder in the UK Biobank.BJPsych Open. 2025 May 9;11(3):e97. doi: 10.1192/bjo.2025.43. BJPsych Open. 2025. PMID: 40341140 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of gene dosage on cognitive ability: A function-based association study across brain and non-brain processes.Cell Genom. 2024 Dec 11;4(12):100721. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2024.100721. Cell Genom. 2024. PMID: 39667348 Free PMC article.
-
Intergenerational transmission of polygenic predisposition for neuropsychiatric traits on emotional and behavioural difficulties in childhood.Nat Commun. 2025 Mar 18;16(1):2674. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57694-w. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40102402 Free PMC article.
-
Polygenic scores stratify neurodevelopmental copy number variant carrier cognitive outcomes in the UK Biobank.NPJ Genom Med. 2024 Sep 28;9(1):43. doi: 10.1038/s41525-024-00426-8. NPJ Genom Med. 2024. PMID: 39341812 Free PMC article.
-
The interplay between genomic copy number variants, sleep, and cognition in the general population.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 19:rs.3.rs-5200475. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5200475/v1. Res Sq. 2025. PMID: 40166003 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Freeman JL, Perry GH, Feuk L, Redon R, McCarroll SA, Altshuler DM, et al. (2006): Copy number variation: new insights in genome diversity. Genome research. 16:949–961. - PubMed
-
- Zarrei M, MacDonald JR, Merico D, Scherer SW (2015): A copy number variation map of the human genome. Nature reviews genetics. 16:172–183. - PubMed
-
- Merikangas AK, Corvin AP, Gallagher L (2009): Copy-number variants in neurodevelopmental disorders: promises and challenges. Trends in genetics. 25:536–544. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

