Intrafusal-fiber LRP4 for muscle spindle formation and maintenance in adult and aged animals
- PMID: 36765071
- PMCID: PMC9918736
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-36454-8
Intrafusal-fiber LRP4 for muscle spindle formation and maintenance in adult and aged animals
Abstract
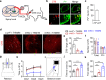
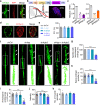
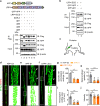
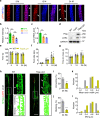
Proprioception is sensed by muscle spindles for precise locomotion and body posture. Unlike the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) for muscle contraction which has been well studied, mechanisms of spindle formation are not well understood. Here we show that sensory nerve terminals are disrupted by the mutation of Lrp4, a gene required for NMJ formation; inducible knockout of Lrp4 in adult mice impairs sensory synapses and movement coordination, suggesting that LRP4 is required for spindle formation and maintenance. LRP4 is critical to the expression of Egr3 during development; in adult mice, it interacts in trans with APP and APLP2 on sensory terminals. Finally, spindle sensory endings and function are impaired in aged mice, deficits that could be diminished by LRP4 expression. These observations uncovered LRP4 as an unexpected regulator of muscle spindle formation and maintenance in adult and aged animals and shed light on potential pathological mechanisms of abnormal muscle proprioception.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
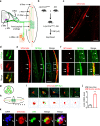
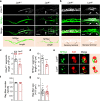
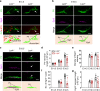
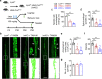
References
-
- Li L, Xiong WC, Mei L. Neuromuscular junction formation, aging, and disorders. Annu Rev. Physiol. 2018;80:159–188. - PubMed
-
- Cohen LA. Analysis of position sense in human shoulder. J. Neurophysiol. 1958;21:550–562. - PubMed
-
- McCloskey DI. Kinesthetic sensibility. Physiol. Rev. 1978;58:763–820. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

