Loss of phosphatase CTDNEP1 potentiates aggressive medulloblastoma by triggering MYC amplification and genomic instability
- PMID: 36765089
- PMCID: PMC9918503
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-36400-8
Loss of phosphatase CTDNEP1 potentiates aggressive medulloblastoma by triggering MYC amplification and genomic instability
Abstract
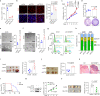
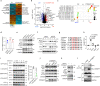
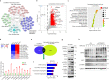
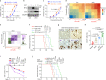
MYC-driven medulloblastomas are highly aggressive childhood brain tumors, however, the molecular and genetic events triggering MYC amplification and malignant transformation remain elusive. Here we report that mutations in CTDNEP1, a CTD nuclear-envelope-phosphatase, are the most significantly enriched recurrent alterations in MYC-driven medulloblastomas, and define high-risk subsets with poorer prognosis. Ctdnep1 ablation promotes the transformation of murine cerebellar progenitors into Myc-amplified medulloblastomas, resembling their human counterparts. CTDNEP1 deficiency stabilizes and activates MYC activity by elevating MYC serine-62 phosphorylation, and triggers chromosomal instability to induce p53 loss and Myc amplifications. Further, phosphoproteomics reveals that CTDNEP1 post-translationally modulates the activities of key regulators for chromosome segregation and mitotic checkpoint regulators including topoisomerase TOP2A and checkpoint kinase CHEK1. Co-targeting MYC and CHEK1 activities synergistically inhibits CTDNEP1-deficient MYC-amplified tumor growth and prolongs animal survival. Together, our studies demonstrate that CTDNEP1 is a tumor suppressor in highly aggressive MYC-driven medulloblastomas by controlling MYC activity and mitotic fidelity, pointing to a CTDNEP1-dependent targetable therapeutic vulnerability.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Liu KW, Pajtler KW, Worst BC, Pfister SM, Wechsler-Reya RJ. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets in pediatric brain tumors. Sci. Signal. 2017;10:eaaf7593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

