Cyclists' exposure to air pollution, noise, and greenery: a population-level spatial analysis approach
- PMID: 36765331
- PMCID: PMC9921333
- DOI: 10.1186/s12942-023-00326-7
Cyclists' exposure to air pollution, noise, and greenery: a population-level spatial analysis approach
Abstract
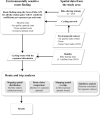
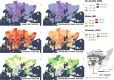
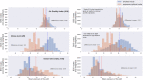
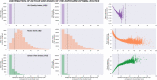
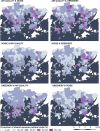
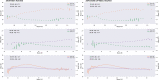
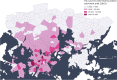
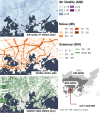
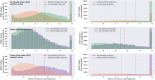
Urban travel exposes people to a range of environmental qualities with significant health and wellbeing impacts. Nevertheless, the understanding of travel-related environmental exposure has remained limited. Here, we present a novel approach for population-level assessment of multiple environmental exposure for active travel. It enables analyses of (1) urban scale exposure variation, (2) alternative routes' potential to improve exposure levels per exposure type, and (3) by combining multiple exposures. We demonstrate the approach's feasibility by analysing cyclists' air pollution, noise, and greenery exposure in Helsinki, Finland. We apply an in-house developed route-planning and exposure assessment software and integrate to the analysis 3.1 million cycling trips from the local bike-sharing system. We show that especially noise exposure from cycling exceeds healthy thresholds, but that cyclists can influence their exposure by route choice. The proposed approach enables planners and individual citizens to identify (un)healthy travel environments from the exposure perspective, and to compare areas in respect to how well their environmental quality supports active travel. Transferable open tools and data further support the implementation of the approach in other cities.
Keywords: Active travel; Air pollution; Environmental exposure; Greenery; Noise; Route choice.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Nieuwenhuijsen MJ. Urban and transport planning pathways to carbon neutral, liveable and healthy cities: a review of the current evidence. Environ Int. 2020;140:105661. - PubMed
-
- Badland H, Pearce J. Liveable for whom? Prospects of urban liveability to address health inequities. Soc Sci Med. 2019;232:94–105. - PubMed
-
- EEA. Healthy environment, healthy lives: how the environment influences health and well-being in Europe. 2020.
-
- WHO. World Health Statistics 2018: Monitoring health for the SDGs. Geneva; 2018. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/272596/9789241565585-en.... Accessed 5 May 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

