Effect of omega-3 supplementation on lipid profile in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
- PMID: 36765362
- PMCID: PMC9912483
- DOI: 10.1186/s12937-022-00826-5
Effect of omega-3 supplementation on lipid profile in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Abstract
Purpose: Dyslipidemia is considered as a known risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Yet various trials with wide ranges of doses and durations have reported contradictory results. We undertook this meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to determine whether omega-3 supplementation can affect lipid profile in children and adolescents.
Methods: Cochrane Library, Embase, PubMed, and Scopus databases were searched up to March 2021. Meta-analysis was performed using random-effect method. Effect size was expressed as weighted mean difference (WMD) and 95% confidence interval (CI). Heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 index. In order to identification of potential sources of heterogeneity, predefined subgroup and meta-regression analysis was conducted.
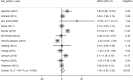
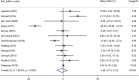
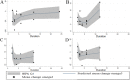
Results: A total of 14 RCTs with 15 data sets were included. Based on the combination of effect sizes, there was a significant reduction in TG levels (WMD: -15.71 mg/dl, 95% CI: -25.76 to -5.65, P=0.002), with remarkable heterogeneity (I2=88.3%, P<0.001). However, subgroup analysis revealed that omega-3 supplementation significantly decreased TG only in studies conducted on participants ≤13 years old (WMD=-25.09, 95% CI: -43.29 to -6.90, P=0.007), (I2=84.6%, P<0.001) and those with hypertriglyceridemia (WMD=-28.26, 95% CI: -39.12 to -17.41, P<0.001), (I2=0.0%, P=0.934). Omega-3 supplementation had no significant effect on total cholesterol, HDL, and LDL levels. Also, results of nonlinear analysis showed significant effect of treatment duration on HDL status (Pnon-linearity=0.047).
Conclusion: Omega-3 supplementation may significantly reduce TG levels in younger children and those with hypertriglyceridemia. Also, based on the HDL-related results, clinical trials with longer duration of intervention are recommended in this population.
Keywords: Children; Lipid profile; Meta-analysis; Omega-3; Systematic review.
© 2023. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
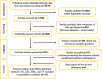
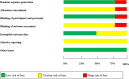
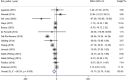
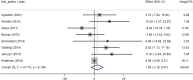
Similar articles
-
The effect of vitamin D on the lipid profile as a risk factor for coronary heart disease in postmenopausal women: a meta-analysis and systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Exp Gerontol. 2022 May;161:111709. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2022.111709. Epub 2022 Jan 26. Exp Gerontol. 2022. PMID: 35090975
-
Effects of sumac supplementation on lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Phytother Res. 2024 Jan;38(1):241-252. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8046. Epub 2023 Oct 21. Phytother Res. 2024. PMID: 37864474
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional interventions for survivors of childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 22;2016(8):CD009678. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009678.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27545902 Free PMC article.
-
Does Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation Have Favorable Effects on the Lipid Profile in Postmenopausal Women? A Systematic Review and Dose-response Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Clin Ther. 2023 Jan;45(1):e74-e87. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2022.12.009. Epub 2023 Jan 12. Clin Ther. 2023. PMID: 36641259
Cited by
-
Fish consumption and its lipid modifying effects - A review of intervention studies.Neurotoxicology. 2023 Dec;99:82-96. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2023.10.003. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Neurotoxicology. 2023. PMID: 37820771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2024 Aug 28;16(8):e68002. doi: 10.7759/cureus.68002. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39347373 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Laslett LJ, Alagona P, Clark BA, Drozda JP, Saldivar F, Wilson SR, et al. The worldwide environment of cardiovascular disease: prevalence, diagnosis, therapy, and policy issues: a report from the American College of Cardiology. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60(25 Supplement):S1–S49. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.11.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

