Poor Mobilizers in Lymphoma but Not Myeloma Patients Had Significantly Poorer Progression-Free Survival after Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation: Results of a Large Retrospective, Single-Center Observational Study
- PMID: 36765566
- PMCID: PMC9913576
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15030608
Poor Mobilizers in Lymphoma but Not Myeloma Patients Had Significantly Poorer Progression-Free Survival after Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation: Results of a Large Retrospective, Single-Center Observational Study
Abstract
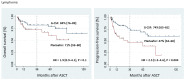
In our single-center study, 357 myeloma and lymphoma patients between 2009 and 2019 were mobilized with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF 7.5 µg/kg bid for four days) plus a fixed dose of 24 mg Plerixafor when indicated (Plerixafor Group, n = 187) or G-CSF alone (G-CSF Group, n = 170). The target CD34 cell yields were ≥2.0 × 106 CD34+ cells/kg in lymphoma and ≥4.0 × 106 CD34+ cells/kg in myeloma patients to enable putative second transplants in the latter. There were no significant differences in engraftment kinetics or transfusion requirements between the Plerixafor Group and the control group in the myeloma cohort, with lymphoma patients not requiring Plerixafor showing significantly faster neutrophil recovery, a trend to faster platelet recovery, and a significantly lower need for platelet transfusions, probably due to the significantly lower number of CD34-positive cells re-transfused. While in myeloma patients the outcome (overall survival, progression-free survival) following autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) was similar between the Plerixafor Group and the control group, hard to mobilize lymphoma patients had significantly poorer progression-free survival (47% vs. 74% at 36 months after ASCT, p = 0.003) with a trend also to poorer overall survival (71% vs. 84%). In conclusion, while there seem to be no differences in stemness capacity and long-term engraftment efficiency between the Plerixafor and the G-CSF Group in lymphoma as well as myeloma patients, poor mobilizing lymphoma patients per se constitute a high-risk population with a poorer outcome after ASCT. Whether disease characteristics and/or a more intense or stem cell-toxic pre-mobilization chemo-/radiotherapy burden in this cohort are responsible for this observation remains to be shown in future studies.
Keywords: Plerixafor; autologous stem cell transplantation; granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; lymphoma; multiple myeloma; poor mobilizer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dhakal B., Szabo A., Chabra S., Hamadani M., D’Souza A., Usmani S., Sieracki R., Gyawali B., Jackson J., Asimakopoulos F., et al. Autologous Transplantation for Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma in the Era of Novel Agent Induction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4:343–350. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.4600. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gay F., Engelhardt M., Terpos E., Wäsch R., Giaccone L., Auner H., Caers J., Gramatzki M., van de Donk N., Oliva S., et al. From Transplant to Novel Cellular Therapies in Multiple Myeloma: European Myeloma Network Guidelines and Future Perspectives. Haematologica. 2018;103:197–211. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2017.174573. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources