Increased Prevalence of EBV Infection in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients: A Six-Year Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 36765601
- PMCID: PMC9913071
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15030643
Increased Prevalence of EBV Infection in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients: A Six-Year Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
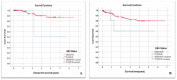
Epstein Barr Virus (EBV) is implicated in the carcinogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) and currently associated with at least 1% of global cancers. The differential prognosis analysis of NPC in EBV genotypes remains to be elucidated. Medical, radiological, pathological, and laboratory reports of 146 NPC patients were collected retrospectively over a 6-year period between 2015 and 2020. From the pathology archives, DNA was extracted from tumor blocks and used for EBV nuclear antigen 3C (EBNA-3C) genotyping by nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR). We found a high prevalence of 96% of EBV infection in NPC patients with a predominance of genotype I detected in 73% of NPC samples. Histopathological examination showed that most of the NPC patients were in the advanced stages of cancer: stage III (38.4%) or stage IV-B (37.7%). Only keratinized squamous cell carcinoma was significantly higher in EBV negative NPC patients compared with those who were EBV positive (OR = 0.01, 95%CI = (0.004-0.32; p = 0.009)), whereas the majority of patients (91.8%) had undifferentiated, non-keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma, followed by differentiated, non-keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma (7.5%). Although NPC had metastasized to 16% of other body sites, it was not associated with EBV infection, except for lung metastasis. A statistically significant reverse association was observed between EBV infection and lung metastasis (OR = 0.07, 95%CI = (0.01-0.51; p = 0.008)). Although 13% of NPC patients died, the overall survival (OS) mean time was 5.59 years. Given the high prevalence of EBV-associated NPC in our population, Saudi could be considered as an area with a high incidence of EBV-associated NPC with a predominance of EBV genotype I. A future multi-center study with a larger sample size is needed to assess the true burden of EBV-associated NPC in Saudi Arabia.
Keywords: EBV; NPC; Saudi Arabia; epidemiology; genotyping; prevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Fierti A.O., Yakass M.B., Okertchiri E.A., Adadey S.M., Quaye O. The Role of Epstein-Barr Virus in Modulating Key Tumor Suppressor Genes in Associated Malignancies: Epigenetics, Transcriptional, and Post-Translational Modifications. Biomolecules. 2022;12:127. doi: 10.3390/biom12010127. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alotaibi A.D., Ahmed H.G., Elasbali A.M. Nasopharyngeal cancer in Saudi Arabia: Epidemiology and possible risk factors. J. Oncol. Sci. 2019;5:23–30. doi: 10.1016/j.jons.2019.01.002. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

