In Vitro Measurement and Mathematical Modeling of Thermally-Induced Injury in Pancreatic Cancer Cells
- PMID: 36765619
- PMCID: PMC9913239
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15030655
In Vitro Measurement and Mathematical Modeling of Thermally-Induced Injury in Pancreatic Cancer Cells
Abstract
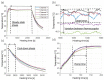
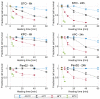
Thermal therapies are under investigation as part of multi-modality strategies for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. In the present study, we determined the kinetics of thermal injury to pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and evaluated predictive models for thermal injury. Cell viability was measured in two murine pancreatic cancer cell lines (KPC, Pan02) and a normal fibroblast (STO) cell line following in vitro heating in the range 42.5-50 °C for 3-60 min. Based on measured viability data, the kinetic parameters of thermal injury were used to predict the extent of heat-induced damage. Of the three thermal injury models considered in this study, the Arrhenius model with time delay provided the most accurate prediction (root mean square error = 8.48%) for all cell lines. Pan02 and STO cells were the most resistant and susceptible to hyperthermia treatments, respectively. The presented data may contribute to studies investigating the use of thermal therapies as part of pancreatic cancer treatment strategies and inform the design of treatment planning strategies.
Keywords: Arrhenius injury model; cell death; hyperthermia; pancreatic cancer; thermal damage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) Annual Report to the Nation: Cancer Deaths Continue Downward Trend; Modest Improvements in Survival for Pancreatic Cancer. 27 October 2022. [(accessed on 10 November 2022)]; Available online: https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/annual-report-nation-cance....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

