Incidental Diagnosis of Urothelial Bladder Cancer: Associations with Overall Survival
- PMID: 36765629
- PMCID: PMC9913049
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15030668
Incidental Diagnosis of Urothelial Bladder Cancer: Associations with Overall Survival
Abstract
Background: We investigated whether an incidental diagnosis (ID) of bladder cancer (BC) was associated with improved survival.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed data of consecutive patients with no prior diagnosis of urothelial cancer who underwent a primary transurethral resection of bladder tumor (pTURBT) between January 2013 and February 2021 and were subsequently diagnosed with urothelial BC. The type of diagnosis (incidental or non-incidental) was identified. Overall, relative, recurrence-free, and progression-free survival rates (OS, RS, RFS, and PFS) after pTURBT were evaluated using the Kaplan-Meier curves and long-rank tests. A multivariable Cox regression model for the overall mortality was developed.
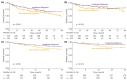
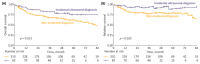
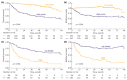
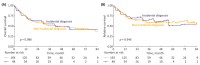
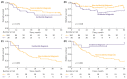
Results: A total of 435 patients were enrolled. The median follow-up was 2.7 years. ID cases were more likely to be low-grade (LG) and non-muscle-invasive. ID vs. non-ID was associated with a trend toward an improved 7-year OS (66% vs. 49%, p = 0.092) and a significantly improved 7-year OS, if incidental cases were limited to ultrasound-detected tumors (75% vs. 49%, p = 0.013). ID was associated with improved survival among muscle-invasive BC (MIBC) patients (3-year RS: 97% vs. 23%, p < 0.001), but not among other subgroups stratified according to disease stage or grade. In multivariable analysis, only age, MIBC, and high-grade (HG) cancer demonstrated an association with mortality. PFS and RFS among non-MIBC patients did not differ in regard to the type of diagnosis.
Conclusions: Incidental diagnosis may contribute to an improved survival in BC patients, most probably in the mechanism of the relative downgrading of the disease, including the possible overdiagnosis of LG tumors. Nevertheless, in the subgroup analyses, we noted marked survival benefits in MIBC cases. Further prospective studies are warranted to gain a deeper understanding of the observed associations.
Keywords: bladder cancer; incidental diagnosis; screening; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Safiri S., Kolahi A.-A., Naghavi M. Global, regional and national burden of bladder cancer and its attributable risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease study 2019. BMJ Glob. Health. 2021;6:e004128. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2020-004128. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cambier S., Sylvester R.J., Collette L., Gontero P., Brausi M.A., van Andel G., Kirkels W.J., Da Silva F.C., Oosterlinck W., Prescott S., et al. EORTC Nomograms and Risk Groups for Predicting Recurrence, Progression, and Disease-specific and Overall Survival in Non–Muscle-invasive Stage Ta–T1 Urothelial Bladder Cancer Patients Treated with 1–3 Years of Maintenance Bacillus Calmette-Guérin. Eur. Urol. 2016;69:60–69. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.06.045. - DOI - PubMed
-
- International Collaboration of Trialists. Medical Research Council Advanced Bladder Cancer Working Party (now the National Cancer Research Institute Bladder Cancer Clinical Studies Group) European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Genito-Urinary Tract Cancer Group. Australian Bladder Cancer Study Group. National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Finnbladder. Norwegian Bladder Cancer Study Group. Club Urologico Espanol de Tratamiento Oncologico Group. Griffiths G., Hall R., et al. International phase III trial assessing neoadjuvant cisplatin, methotrexate, and vinblastine chemotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Long-term results of the BA06 30894 trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011;29:2171–2177. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

