Orthovoltage X-ray Minibeam Radiation Therapy for the Treatment of Ocular Tumours-An In Silico Evaluation
- PMID: 36765637
- PMCID: PMC9913874
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15030679
Orthovoltage X-ray Minibeam Radiation Therapy for the Treatment of Ocular Tumours-An In Silico Evaluation
Abstract
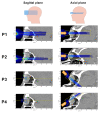
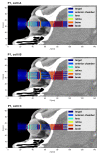
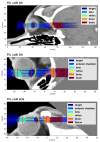
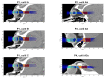
(1) Background: Radiotherapeutic treatments of ocular tumors are often challenging because of nearby radiosensitive structures and the high doses required to treat radioresistant cancers such as uveal melanomas. Although increased local control rates can be obtained with advanced techniques such as proton therapy and stereotactic radiosurgery, these modalities are not always accessible to patients (due to high costs or low availability) and side effects in structures such as the lens, eyelids or anterior chamber remain an issue. Minibeam radiation therapy (MBRT) could represent a promising alternative in this regard. MBRT is an innovative new treatment approach where the irradiation field is composed of multiple sub-millimetric beamlets, spaced apart by a few millimetres. This creates a so-called spatial fractionation of the dose which, in small animal experiments, has been shown to increase normal tissue sparing while simultaneously providing high tumour control rates. Moreover, MBRT with orthovoltage X-rays could be easily implemented in widely available and comparably inexpensive irradiation platforms. (2) Methods: Monte Carlo simulations were performed using the TOPAS toolkit to evaluate orthovoltage X-ray MBRT as a potential alternative for treating ocular tumours. Dose distributions were simulated in CT images of a human head, considering six different irradiation configurations. (3) Results: The mean, peak and valley doses were assessed in a generic target region and in different organs at risk. The obtained doses were comparable to those reported in previous X-ray MBRT animal studies where good normal tissue sparing and tumour control (rat glioma models) were found. (4) Conclusions: A proof-of-concept study for the application of orthovoltage X-ray MBRT to ocular tumours was performed. The simulation results encourage the realisation of dedicated animal studies considering minibeam irradiations of the eye to specifically assess ocular and orbital toxicities as well as tumour response. If proven successful, orthovoltage X-ray minibeams could become a cost-effective treatment alternative, in particular for developing countries.
Keywords: MBRT; Monte Carlo simulation; X-rays; cost-effective; in silico; minibeams; ocular tumours; orthovoltage.
Conflict of interest statement
Y.P. holds a patent on the implementation of X-ray MBRT using the SARRP platform under the US patent number USBR16CNRRAD/sl and the international patent number PCT/EP2017/078096.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Minibeam radiation therapy: A micro- and nano-dosimetry Monte Carlo study.Med Phys. 2020 Mar;47(3):1379-1390. doi: 10.1002/mp.14009. Epub 2020 Jan 28. Med Phys. 2020. PMID: 31900944
-
Improving the dose distributions in minibeam radiation therapy: Helium ions vs protons.Med Phys. 2019 Aug;46(8):3640-3648. doi: 10.1002/mp.13646. Epub 2019 Jun 25. Med Phys. 2019. PMID: 31173369
-
Theoretical dosimetric evaluation of carbon and oxygen minibeam radiation therapy.Med Phys. 2017 May;44(5):1921-1929. doi: 10.1002/mp.12175. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Med Phys. 2017. PMID: 28236644
-
Spatial fractionation of the dose in proton therapy: Proton minibeam radiation therapy.Cancer Radiother. 2019 Oct;23(6-7):677-681. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2019.08.001. Epub 2019 Sep 4. Cancer Radiother. 2019. PMID: 31494038 Review.
-
Technical aspects of proton minibeam radiation therapy: Minibeam generation and delivery.Phys Med. 2022 Aug;100:64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2022.06.010. Epub 2022 Jun 21. Phys Med. 2022. PMID: 35750002 Review.
Cited by
-
Experimental investigation of oxygen diffusion in the peak and valley region of minibeam patterns during x-ray irradiation.Med Phys. 2025 Aug;52(8):e17999. doi: 10.1002/mp.17999. Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40781834 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dendale R., Lumbroso-Le Rouic L., Noel G., Feuvret L., Levy C., Delacroix S., Meyer A., Nauraye C., Mazal A., Mammar H., et al. Proton beam radiotherapy for uveal melanoma: Results of Curie Institut-Orsay proton therapy center (ICPO) Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006;65:780–787. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.01.020. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

