Performance of Radiomics in Microvascular Invasion Risk Stratification and Prognostic Assessment in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36765701
- PMCID: PMC9913680
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15030743
Performance of Radiomics in Microvascular Invasion Risk Stratification and Prognostic Assessment in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Primary liver cancer is the sixth most commonly diagnosed cancer and the third leading cause of cancer death. Advances in phenomenal imaging are paving the way for application in diagnosis and research. The poor prognosis of advanced HCC warrants a personalized approach. The objective was to assess the value of imaging phenomics for risk stratification and prognostication of HCC.
Methods: We performed a meta-analysis of manuscripts published to January 2023 on MEDLINE addressing the value of imaging phenomics for HCC risk stratification and prognostication. Publication information for each were collected using a standardized data extraction form.
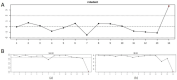
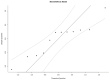
Results: Twenty-seven articles were analyzed. Our study shows the importance of imaging phenomics in HCC MVI prediction. When the training and validation datasets were analyzed separately by the random-effects model, in the training datasets, radiomics had good MVI prediction (AUC of 0.81 (95% CI 0.76-0.86)). Similar results were found in the validation datasets (AUC of 0.79 (95% CI 0.72-0.85)). Using the fixed effects model, the mean AUC of all datasets was 0.80 (95% CI 0.76-0.84).
Conclusions: Imaging phenomics is an effective solution to predict microvascular invasion risk, prognosis, and treatment response in patients with HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; imaging phenomics; radiomics; risk stratification and prognostication.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Yan Liu is an employee of Median Technology. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre . The Nordic Cochrane Centre; Copenhagen, Denmark: 2014. The Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager (RevMan) [Computer Program], Version 5.3.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

