Nutritional, Physicochemical, Microstructural, Rheological, and Organoleptical Characteristics of Ice Cream Incorporating Adansonia digitata Pulp Flour
- PMID: 36766062
- PMCID: PMC9913908
- DOI: 10.3390/foods12030533
Nutritional, Physicochemical, Microstructural, Rheological, and Organoleptical Characteristics of Ice Cream Incorporating Adansonia digitata Pulp Flour
Abstract
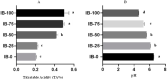
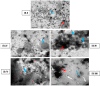
Ice cream's appeal is unrivaled. Nonmilk and milk ingredients in ice cream formulas affect their nutritional value, structure, and organoleptical qualities. Seeking novel dietary ingredients instead of artificial flavoring compounds is vital for improving ice cream taste preference, adding antioxidants, and increasing nutritional value. The current study examines the feasibility of manufacturing a new flavored ice cream with excellent dietary value using Adansonia digitata L. (Baobab) fruit pulp (ADFP). The prepared ice cream's physicochemical and microbiological quality, and rheological, microstructural, and organoleptic properties were investigated. Using ADFP instead of skim milk powder with a partial or complete replacement, five ice cream samples were produced and marked as IB-0, IB-25, IB-50, IB-75, and IB-100. Chemical characteristics were not noticeably impacted except protein and ash, which considerably decreased with increasing ADFP levels. Increasing ADFP in the samples increased titratable acidity and reduced pH. All ice cream samples were microbiologically acceptable with no pathogenic bacteria. By increasing ADFP in the samples, the daily values (%DV) of sodium, potassium, and magnesium were not considerably affected. Calcium reduced from 14.91% in IB-0 to 7.75% in IB-100. All microelements found in the study rose considerably as ADFP increased. Increasing ADFP levels significantly boosted antioxidant levels. The IB-100 sample had the highest total phenolic content (149.29 mg GAE 100 g-1), antioxidant activity (98.12 µmol of TE 100 g-1), total flavonoids (5.96 mg QE 100 g-1), and total flavanols (4.01 mg QE 100 g-1). The inclusion of ADFP had a beneficial effect on the color of the samples. It did not negatively affect the ice cream's organoleptic acceptability as determined by organoleptic, rheological, and microstructural examinations. Interestingly, when skim milk powder was replaced with 50% and 75%, the hardness, viscosity, and aqueous phase separation were significantly improved. In conclusion, ADPF improves the nutritional value of ice cream and can be used as a natural coloring ingredient without affecting microstructural and rheological properties.
Keywords: Adansonia digitata; antioxidants; ice cream; microstructure; nutrition; rheology.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Assessment of using sweet lupine flour as a rich source of carbohydrates and proteins on the biological and quality characteristics of low-fat ice cream.Food Chem. 2025 Sep 1;485:144562. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2025.144562. Epub 2025 Apr 28. Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 40328172
-
Nutritional and Rheological Characteristics of Composite Flour Substituted with Baobab (Adansonia digitata L.) Pulp Flour for Cake Manufacturing and Organoleptic Properties of Their Prepared Cakes.Foods. 2021 Mar 27;10(4):716. doi: 10.3390/foods10040716. Foods. 2021. PMID: 33801774 Free PMC article.
-
Physicochemical, Antioxidant Characteristics and Sensory Evaluation of Functional Pro-Biogenic Ice Cream.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Dec 1;13(1):e4619. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4619. eCollection 2025 Jan. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39803295 Free PMC article.
-
Adansonia digitata L. (Baobab) Bioactive Compounds, Biological Activities, and the Potential Effect on Glycemia: A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2023 May 1;15(9):2170. doi: 10.3390/nu15092170. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37432337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in the application of microbial transglutaminase crosslinking in cheese and ice cream products: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Feb;107(Pt B):2364-2374. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.10.115. Epub 2017 Oct 18. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 29055708 Review.
Cited by
-
The Potential Uses of Baobab Tree's Medicinal Effects in Dentistry: A Literature Review.Cureus. 2023 Nov 23;15(11):e49304. doi: 10.7759/cureus.49304. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38957190 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Villava F.J., Cravero Bruneri A.P., Vinderola G., Goncalvez De Oliveira E., PAZ N.F., Ramon A.N. Formulation of a Peach Ice Cream as Potential Symbiotic Food. Food Sci. Technol. 2017;37:456–461. doi: 10.1590/1678-457x.19716. - DOI
-
- Thorning T.K., Bertram H.C., Bonjour J.-P., De Groot L., Dupont D., Feeney E., Ipsen R., Lecerf J.M., Mackie A., McKinley M.C. Whole Dairy Matrix or Single Nutrients in Assessment of Health Effects: Current Evidence and Knowledge Gaps. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017;105:1033–1045. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.116.151548. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sun-Waterhouse D. The Development of Fruit-Based Functional Foods Targeting the Health and Wellness Market: A Review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011;46:899–920. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2010.02499.x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

