Bati Butter as a Potential Substrate for Lipase Production by Aspergillus terreus NRRL-255
- PMID: 36766093
- PMCID: PMC9914599
- DOI: 10.3390/foods12030564
Bati Butter as a Potential Substrate for Lipase Production by Aspergillus terreus NRRL-255
Abstract
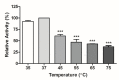
This study evaluated bati butter (Ouratea parviflora) as a substrate for lipase production by solid-state fermentation (SSF) using Aspergillus terreus NRRL-255. A gas chromatograph with a flame ionization detector determined the bati butter fatty acid profile. Lipase production and spore count were optimized using a 32 experimental design and evaluated using the response surface methodology. Moreover, the crude enzyme extract was evaluated against different pH, temperature, and activating and inhibitors reagents. Regarding the fatty acids identified, long-chain accounted for 78.60% of the total lipids. The highest lipase production was obtained at 35 °C and 120 h of fermentation, yielding 216.9 U g-1. Crude enzyme extract presented more significant activity at 37 °C and pH 9. β-Mercaptoethanol increased the enzyme activity (113.80%), while sodium dodecyl sulfate inactivated the enzyme. Therefore, bati butter proved to be a potential substrate capable of inducing lipase production by solid-state fermentation.
Keywords: Ouratea parviflora; enzyme; experimental design; solid-state fermentation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Turning cacay butter and wheat bran into substrate for lipase production by Aspergillus terreus NRRL-255.Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2020;50(7):689-696. doi: 10.1080/10826068.2020.1728698. Epub 2020 Feb 17. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32065557
-
Characterization of biotechnologically relevant extracellular lipase produced by Aspergillus terreus NCFT 4269.10.Braz J Microbiol. 2016 Jan-Mar;47(1):143-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bjm.2015.11.026. Epub 2016 Jan 27. Braz J Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26887237 Free PMC article.
-
Solid-state fermentation of Jatropha seed cake for optimization of lipase, protease and detoxification of anti-nutrients in Jatropha seed cake using Aspergillus versicolor CJS-98.J Biosci Bioeng. 2014 Feb;117(2):208-214. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Aug 16. J Biosci Bioeng. 2014. PMID: 23958640
-
Laundry Detergent Compatibility and Dehairing Efficiency of Alkaline Thermostable Protease Produced from Aspergillus terreus under Solid-state Fermentation.J Oleo Sci. 2020;69(3):241-254. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess19315. J Oleo Sci. 2020. PMID: 32115548
-
Valorization of Palm Oil Industrial Waste as Feedstock for Lipase Production.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2016 Jun;179(4):558-71. doi: 10.1007/s12010-016-2013-z. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26892007
Cited by
-
Developing a cosmetic formulation containing lipase produced by the fungus Aspergillus terreus.PLoS One. 2025 May 7;20(5):e0322106. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322106. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40334180 Free PMC article.
References
-
- do Nascimento J.E.T., de Morais S.M., de Lisboa D.S., de Oliveira Sousa M., Santos S.A.A.R., Magalhães F.E.A., Campos A.R. The Orofacial Antinociceptive Effect of Kaempferol-3-O-Rutinoside, Isolated from the Plant Ouratea Fieldingiana, on Adult Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018;107:1030–1036. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.089. - DOI - PubMed
-
- de Castro H.F., Mendes A.A., dos Santos J.C., de Aguiar C.L. Modificação de Óleos e Gorduras Por Biotransformação. Quim. Nova. 2004;27:146–156. doi: 10.1590/S0100-40422004000100025. - DOI
-
- Hou C.T., Shimada Y. Lipases. Encycl. Microbiol. Third edition. 2009:385–392. doi: 10.1016/B978-012373944-5.00153-X. - DOI
-
- Hasan F., Shah A.A., Hameed A. Industrial Applications of Microbial Lipases. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2006;39:235–251. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.10.016. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

