In Vitro Evaluations and Comparison of the Efficacy of Two Commercial Products Containing Condensed Tannins and of Saifoin (Onobrychis viciifolia Scop.) Hay against Gastrointestinal Nematodes of Goats
- PMID: 36766435
- PMCID: PMC9913204
- DOI: 10.3390/ani13030547
In Vitro Evaluations and Comparison of the Efficacy of Two Commercial Products Containing Condensed Tannins and of Saifoin (Onobrychis viciifolia Scop.) Hay against Gastrointestinal Nematodes of Goats
Abstract
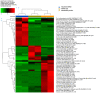
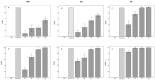
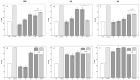
Gastrointestinal nematodes (GINs) is a limiting health factor for dairy goats, and the integration of the diet with fodder containing condensed tannins (CT) is becoming increasingly important to control GINs. To preliminary evaluate their potential role as part of GIN control in goat breeding, the in vitro anthelmintic efficacy of the CTs of Silvafeed BYPRO (SBP), Silvafeed Q powder (SQ), and sainfoin hay (SH) was evaluated, and the untargeted metabolomics profiling of the selected formulations was performed. CTs were extracted in water and in ethanol, their concentration was determined, and their chemical characterization was conducted using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) coupled to High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (HRMS) platform. The in vitro anthelmintic activity of the extracts was evaluated using the Eggs Hatch Test (EHT) and the Larval Migration Inhibition Test (LMIT) using different extract concentrations (150, 300, 600, and 1200 μg/mL). The metabolomic profile of the ethanol extract showed a high number of flavonoids, while the water extract showed higher levels of hydrolysable tannins. The ethanol extracts were effective on both eggs hatching and larvae migration at low concentrations (150 μg/mL) for the three analyzed samples, while the water extracts showed more varied results: SH showed the greatest ovicidal efficacy (concentration 150 μg/mL, %IH = 40.9), while SBP and SQ were more effective against the larvae migration (concentration 600 μg/mL, %LMI = 69.7% and 88%), respectively. The integration of CT-rich fodder into the diet may be considered for the control of GIN infection in goats.
Keywords: Eggs Hatch Test (EHT); Larval Migration Inhibition Test (LMIT); condensed tannins; gastrointestinal nematodes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Di Cerbo A.R., Manfredi M.T., Zanzani S., Stradiotto K. Gastrointestinal infection in goat farms in Lombardy (Northern Italy): Analysis on community and spatial distribution of parasites. Small Rumin. Res. 2010;88:102–112. doi: 10.1016/j.smallrumres.2009.12.017. - DOI
-
- Alberti E., Zanzani S., Ferrari N., Bruni G., Manfredi M. Effects of gastrointestinal nematodes on milk productivity in three dairy goat breeds. Small Rumin. Res. 2012;106:S12–S17. doi: 10.1016/j.smallrumres.2012.04.027. - DOI
-
- Vineer H.R., Morgan E.R., Hertzberg H., Bartley D.J., Bosco A., Charlier J., Chartier C., Claerebout E., De Waal T., Hendrickx G., et al. Increasing importance of anthelmintic resistance in European livestock: Creation and meta-analysis of an open database. Parasite. 2020;27:69. doi: 10.1051/parasite/2020062. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bosco A., Kießler J., Amadesi A., Varady M., Hinney B., Ianniello D., Maurelli M.P., Cringoli G., Rinaldi L. The threat of reduced efficacy of anthelmintics against gastrointestinal nematodes in sheep from an area considered anthelmintic resistance-free. Parasites Vectors. 2020;13:1–12. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04329-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

