Development of an Artificial Intelligence-Based Breast Cancer Detection Model by Combining Mammograms and Medical Health Records
- PMID: 36766450
- PMCID: PMC9913958
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13030346
Development of an Artificial Intelligence-Based Breast Cancer Detection Model by Combining Mammograms and Medical Health Records
Abstract
Background: Artificial intelligence (AI)-based computational models that analyze breast cancer have been developed for decades. The present study was implemented to investigate the accuracy and efficiency of combined mammography images and clinical records for breast cancer detection using machine learning and deep learning classifiers.
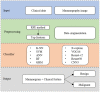
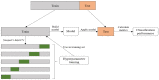
Methods: This study was verified using 731 images from 357 women who underwent at least one mammogram and had clinical records for at least six months before mammography. The model was trained on mammograms and clinical variables to discriminate benign and malignant lesions. Multiple pre-trained deep CNN models to detect cancer in mammograms, including X-ception, VGG16, ResNet-v2, ResNet50, and CNN3 were employed. Machine learning models were constructed using k-nearest neighbor (KNN), support vector machine (SVM), random forest (RF), Artificial Neural Network (ANN), and gradient boosting machine (GBM) in the clinical dataset.
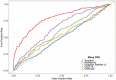
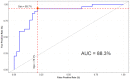
Results: The detection performance obtained an accuracy of 84.5% with a specificity of 78.1% at a sensitivity of 89.7% and an AUC of 0.88. When trained on mammography image data alone, the result achieved a slightly lower score than the combined model (accuracy, 72.5% vs. 84.5%, respectively).
Conclusions: A breast cancer-detection model combining machine learning and deep learning models was performed in this study with a satisfactory result, and this model has potential clinical applications.
Keywords: CNN; Resnet-v2; Resnet50; VGG16; Xception; artificial neural network; breast cancer; gradient boosting machine; k-nearest neighbor; random forest; support vector machine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest regarding this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Dixon A.-M. Diagnostic Breast Imaging: Mammography, Sonography, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, and Interventional Procedures. Ultrasound: J. Br. Med. Ultrasound Soc. 2014;22:182. doi: 10.1177/1742271X14537772. - DOI
-
- Sickles E., D’Orsi C., Bassett L., Appleton C., Berg W., Burnside E. ACR BI-RADS Atlas, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System. 5th ed. American College of Radiology; Reston, VA, USA: 2013.
-
- Ramos-Pollán R., Guevara-López M.A., Suárez-Ortega C., Díaz-Herrero G., Franco-Valiente J.M., Rubio-del-Solar M., González-de-Posada N., Vaz M.A.P., Loureiro J., Ramos I. Discovering mammography-based machine learning classifiers for breast cancer diagnosis. J. Med. Syst. 2012;36:2259–2269. doi: 10.1007/s10916-011-9693-2. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

