Uncertain-CAM: Uncertainty-Based Ensemble Machine Voting for Improved COVID-19 CXR Classification and Explainability
- PMID: 36766546
- PMCID: PMC9914375
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13030441
Uncertain-CAM: Uncertainty-Based Ensemble Machine Voting for Improved COVID-19 CXR Classification and Explainability
Abstract
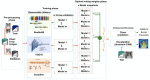
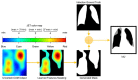
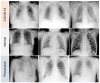
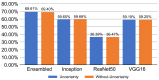
The ongoing coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has had a significant impact on patients and healthcare systems across the world. Distinguishing non-COVID-19 patients from COVID-19 patients at the lowest possible cost and in the earliest stages of the disease is a major issue. Additionally, the implementation of explainable deep learning decisions is another issue, especially in critical fields such as medicine. The study presents a method to train deep learning models and apply an uncertainty-based ensemble voting policy to achieve 99% accuracy in classifying COVID-19 chest X-rays from normal and pneumonia-related infections. We further present a training scheme that integrates the cyclic cosine annealing approach with cross-validation and uncertainty quantification that is measured using prediction interval coverage probability (PICP) as final ensemble voting weights. We also propose the Uncertain-CAM technique, which improves deep learning explainability and provides a more reliable COVID-19 classification system. We introduce a new image processing technique to measure the explainability based on ground-truth, and we compared it with the widely adopted Grad-CAM method.
Keywords: COVID-19; deep learning; explainable AI; intelligent signal processing; uncertainty.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detection of COVID-19 in X-ray Images Using Densely Connected Squeeze Convolutional Neural Network (DCSCNN): Focusing on Interpretability and Explainability of the Black Box Model.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Dec 18;22(24):9983. doi: 10.3390/s22249983. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36560352 Free PMC article.
-
Computer-aided diagnostic for classifying chest X-ray images using deep ensemble learning.BMC Med Imaging. 2022 Oct 15;22(1):178. doi: 10.1186/s12880-022-00904-4. BMC Med Imaging. 2022. PMID: 36243705 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-Net Biochem: an explainability-driven framework to building machine learning models for predicting survival and kidney injury of COVID-19 patients from clinical and biochemistry data.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 9;13(1):17001. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42203-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37813920 Free PMC article.
-
A Deep Learning Model for Diagnosing COVID-19 and Pneumonia through X-ray.Curr Med Imaging. 2023;19(4):333-346. doi: 10.2174/1573405618666220610093740. Curr Med Imaging. 2023. PMID: 35692156
-
Biphasic majority voting-based comparative COVID-19 diagnosis using chest X-ray images.Expert Syst Appl. 2023 Apr 15;216:119430. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.119430. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Expert Syst Appl. 2023. PMID: 36570382 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Towards Improved XAI-Based Epidemiological Research into the Next Potential Pandemic.Life (Basel). 2024 Jun 21;14(7):783. doi: 10.3390/life14070783. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39063538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Performance and explainability of feature selection-boosted tree-based classifiers for COVID-19 detection.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 7;10(1):e23219. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23219. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38170121 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coronavirus Research is Being Published at a Furious Pace. [(accessed on 31 May 2022)]. Available online: https://www.economist.com/graphic-detail/2020/03/20/coronavirus-research....
-
- Brihn A., Chang J., Yong K.O., Balter S., Terashita D., Rubin Z., Yeganeh N. Diagnostic Performance of an Antigen Test with RT-PCR for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in a Hospital Setting—Los Angeles County, California, June–August 2020. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021;70:702–706. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7019a3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hassaballah M., Awad A.I. Deep Learning in Computer Vision: Principles and Applications. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: Taylor and Francis; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

