A-Kinase Anchoring Proteins in Cardiac Myocytes and Their Roles in Regulating Calcium Cycling
- PMID: 36766777
- PMCID: PMC9913689
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12030436
A-Kinase Anchoring Proteins in Cardiac Myocytes and Their Roles in Regulating Calcium Cycling
Abstract
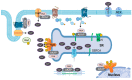
The rate of calcium cycling and calcium transient amplitude are critical determinants for the efficient contraction and relaxation of the heart. Calcium-handling proteins in the cardiac myocyte are altered in heart failure, and restoring the proper function of those proteins is an effective potential therapeutic strategy. The calcium-handling proteins or their regulators are phosphorylated by a cAMP-dependent kinase (PKA), and thereby their activity is regulated. A-Kinase Anchoring Proteins (AKAPs) play a seminal role in orchestrating PKA and cAMP regulators in calcium handling and contractile machinery. This cAMP/PKA orchestration is crucial for the increased force and rate of contraction and relaxation of the heart in response to fight-or-flight. Knockout models and the few available preclinical models proved that the efficient targeting of AKAPs offers potential therapies tailor-made for improving defective calcium cycling. In this review, we highlight important studies that identified AKAPs and their regulatory roles in cardiac myocyte calcium cycling in health and disease.
Keywords: A-kinase anchoring protein; Calcium cycling; Phospholamban; Protein Kinase A; Ryanodine receptor; SERCA2a; cAMP signaling; calcium channel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Scholten A., Poh M.K., van Veen T.A., van Breukelen B., Vos M.A., Heck A.J. Analysis of the cGMP/cAMP interactome using a chemical proteomics approach in mammalian heart tissue validates sphingosine kinase type 1-interacting protein as a genuine and highly abundant AKAP. J. Proteome Res. 2006;5:1435–1447. doi: 10.1021/pr0600529. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

