A Single Session of a Digital Health Tool-Delivered Exercise Intervention May Provide Immediate Relief from Pelvic Pain in Women with Endometriosis: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Study
- PMID: 36767032
- PMCID: PMC9914835
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20031665
A Single Session of a Digital Health Tool-Delivered Exercise Intervention May Provide Immediate Relief from Pelvic Pain in Women with Endometriosis: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Study
Abstract
Background: Endometriosis is a debilitating chronic condition that is commonly associated with chronic pelvic pain, affecting approximately 10% of women of reproductive age worldwide. The general principle of pain management in this population involves both pharmacological and surgical interventions. There is also increasing interest in the use of exercise as an alternative non-pharmacological analgesic, but adherence and accessibility to face-to-face exercise-delivery modalities are poor. This study aims to determine the immediate impact of a single session of 'supervised' telehealth-delivered exercise compared to 'self-managed' virtual reality (VR)-delivered exercise on pelvic pain associated with endometriosis.
Methods: Twenty-two women experiencing pelvic pain due to endometriosis were included and randomized into three groups: (i) VR-delivered exercise group (n = 8); (ii) telehealth-delivered exercise group (n = 8); and (iii) control group (n = 6). The visual analogue scale (VAS) was used to assess the severity of pelvic pain.
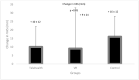
Results: There was no statistically significant between-group difference (p = 0.45) in the participants' pain score following a single session of the study interventions (VR or telehealth) or the control. However, a 'medium-to-large' group x time interaction effect (η2 = 0.10) was detected, indicating a more favorable pain score change following a single session of telehealth- (pre-post ∆: +10 ± 12 mm) and VR-delivered exercise (pre-post ∆: +9 ± 24 mm) compared to the control group (pre-post ∆: +16 ± 12 mm).
Conclusions: Our study suggests that a single bout of a 'self-managed' VR-delivered exercise may be as efficacious as a single session of 'supervised' telehealth-delivered exercise in providing immediate relief from pelvic pain associated with endometriosis.
Keywords: endometriosis; pelvic pain; telehealth; virtual reality; women’s health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Oats J., Abraham S. Llewellyn-Jones Fundamentals of Obstetrics and Gynaecology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2015.
-
- Young E. The cost of endometriosis in Australia: A report for EndoActive by Ernst & Young. EndoActive. 2019;6 unpublished .
-
- Nnoaham K.E., Hummelshoj L., Webster P., d’Hooghe T., de Cicco Nardone F., de Cicco Nardone C., Jenkinson C., Kennedy S.H., Zondervan K.T., World Endometriosis Research Foundation Global Study of Women’s Health consortium Impact of endometriosis on quality of life and work productivity: A multicenter study across ten countries. Fertil. Steril. 2011;96:366–373.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2011.05.090. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical