The Incremental Role of Multiorgan Point-of-Care Ultrasounds in the Emergency Setting
- PMID: 36767456
- PMCID: PMC9915087
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20032088
The Incremental Role of Multiorgan Point-of-Care Ultrasounds in the Emergency Setting
Abstract
Point-of-care ultrasonography (POCUS) represents a goal-directed ultrasound examination performed by clinicians directly involved in patient healthcare. POCUS has been widely used in emergency departments, where US exams allow physicians to make quick diagnoses and to recognize early life-threatening conditions which require prompt interventions. Although initially meant for the real-time evaluation of cardiovascular and respiratory pathologies, its use has been extended to a wide range of clinical applications, such as screening for deep-vein thrombosis and trauma, abdominal ultrasonography of the right upper quadrant and appendix, and guidance for invasive procedures. Moreover, recently, bedside ultrasounds have been used to evaluate the fluid balance and to guide decongestive therapy in acutely decompensated heart failure. The aim of the present review was to discuss the most common applications of POCUS in the emergency setting.
Keywords: POCUS; VE x US; congestion; deep-vein thrombosis (DTV); echocardiography; emergency medicine (EM); lung ultrasound (LUS); point-of-care.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




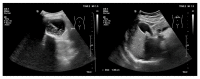
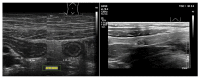

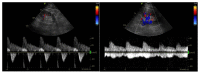
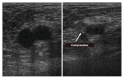
References
-
- Bahner D., Blaivas M., Cohen H.L., Fox J.C., Hoffenberg S., Kendall J., Langer J., McGahan J.P., Sierzenski P., Tayal V.S., et al. AIUM Practice Guideline for the Performance of the Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma (FAST) Examination. J. Ultrasound Med. 2008;27:313–318. doi: 10.7863/jum.2008.27.2.313. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

