Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Psychosocial Well-being and Adaptation in Children and Adolescents with Asperger's Syndrome
- PMID: 36767499
- PMCID: PMC9915274
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20032132
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Psychosocial Well-being and Adaptation in Children and Adolescents with Asperger's Syndrome
Abstract
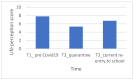
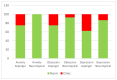
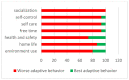
Mental health could worsen in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder during the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition, their parents could be more at risk for an increase in anxiety and depression symptomatology. This study aims to understand the adaptation and the psychosocial well-being in a sample of 16 males aged 10-21 years old with Asperger's syndrome after the quarantine for COVID-19 when they return to school and partially to their activities in September 2020. The adopted approach is multi-informant with a battery of questionnaires on psychological health and adaptation given by a secure online web data Qualtrics both to adolescents and also to their parents. Paralleling matched peers with typical developments were assessed by adopting the same methodology. The results evidenced several difficulties in psychological health in population with Asperger's syndrome, especially in anxiety and socialization. Adaptation is put in crisis, even if they reported a good comprehension and adoption of the right behaviors anti-COVID-19. Parents of children with Asperger's syndrome reported similar psychological difficulties and general health to those of the group of children typically developing. Some clinical indications could be discussed for psychologists who follow children and adolescents with Asperger's syndrome.
Keywords: Asperger’s syndrome; COVID-19; adaptation; adolescents; atypically development; children; multi-informant; parents; typically development; well-being.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC, USA: 2013.
-
- Attwood T. Guida Completa alla Sindrome di Asperger. Edra; Perignano, Italy: 2019.
-
- Baio J., Wiggins L., Christensen D.L., Maenner M.J., Daniels J., Warren Z., Vehorn A., Esler A., Salinas A., Durkin M.S., et al. Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2014. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2018;67:1–23. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss6706a1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang C., Pan R., Wan X., Tan Y., Xu L., Xu L., Ho C.S., Ho R.C. Immediate Psychological Responses and Associated Factors during the Initial Stage of the 2019 Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Epidemic among the General Population in China. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2020;17:1729. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17051729. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

