Impact of Digital Transformation on Enterprise Carbon Intensity: The Moderating Role of Digital Information Resources
- PMID: 36767545
- PMCID: PMC9915449
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20032178
Impact of Digital Transformation on Enterprise Carbon Intensity: The Moderating Role of Digital Information Resources
Abstract
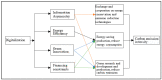
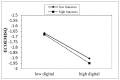
In the context of China's "digital power" strategy, the realization of a green and low-carbon shift in manufacturing has become a necessary condition to promote the economy, and the digital factor has increasingly become a new driving force. The text mining and IPCC methods were used to measure manufacturing enterprise digitalization and the level of enterprise carbon emission intensity from 2011 to 2021, respectively. This study then explored the impact of digitalization on manufacturing enterprise carbon emission intensity based on the least squares method model and instrumental variable method model. This research comes to three conclusions. (1) Digitalization can significantly reduce the enterprise carbon emission intensity of China's manufacturing industry, and the influence shows a "marginal increase." (2) Notably, a mechanism analysis indicates the intermediary effect sizes of four crucial intermediaries: green technology innovation > financing constraint > information asymmetry > energy use efficiency. Interestingly, digital information resources positively moderate the positive effect of digitalization on carbon emission intensity through three paths: financing constraints, green technology innovation, and information asymmetry. (3) The influence shows evident signs of heterogeneity-as environmental regulation, financial development, executive education, and R&D quality advance, the inhibiting effect of digitalization on enterprise carbon emission intensity becomes more pronounced. Finally, corresponding policy suggestions are proposed.
Keywords: carbon emission intensity; digital information resources; digital transformation; financing constraints; green innovation; information asymmetry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Effect of Input Digitalization on Carbon Emission Intensity: An Empirical Analysis Based on China's Manufacturing.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 11;20(4):3174. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20043174. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36833868 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of digital technology innovation on carbon intensity: evidence from China's manufacturing A-share listed enterprises.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Jun;31(28):41084-41106. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-33766-0. Epub 2024 Jun 6. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38842782
-
Does digital economy keep enterprises out of green innovation trouble? evidence from "double carbon" goal.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Aug;31(37):49855-49873. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-34476-3. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 39083177
-
Intelligent Manufacturing Technology in the Steel Industry of China: A Review.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Oct 26;22(21):8194. doi: 10.3390/s22218194. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36365891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of the digital economy on enterprise innovation behavior: Based on CiteSpace knowledge graph analysis.Front Psychol. 2023 Jan 23;14:1031294. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1031294. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 36755669 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Smart Sensors for Subway Electric Motor Escalators through AHP-Gaussian Method.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Apr 20;23(8):4131. doi: 10.3390/s23084131. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37112474 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Input Digitalization on Carbon Emission Intensity: An Empirical Analysis Based on China's Manufacturing.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 11;20(4):3174. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20043174. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36833868 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of green innovation on carbon reduction in China.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 18;14(1):14032. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64554-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38890482 Free PMC article.
-
Can digitalization improve enterprise sustainability?-Evidence from the resilience perspective of Chinese firms.Heliyon. 2023 Mar 16;9(3):e14607. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14607. eCollection 2023 Mar. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36994388 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of digital economy on high-quality economic development: Research based on the consumption expansion.PLoS One. 2023 Dec 15;18(12):e0292925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292925. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38100500 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alharthi M., Hanif I., Alamoudi H. Impact of environmental pollution on human health and financial status of households in MENA countries: Future of using renewable energy to eliminate the environmental pollution. Renew. Energy. 2022;190:338–346. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2022.03.118. - DOI
-
- Hao X., Wang X., Wu H., Hao Y. Path to sustainable development: Does digital economy matter in manufacturing green total factor productivity? Sustain. Dev. 2022;30:787–1450. doi: 10.1002/sd.2397. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources