Randomized Controlled Trial Evaluating the Benefit of a Novel Clinical Decision Support System for the Management of COVID-19 Patients in Home Quarantine: A Study Protocol
- PMID: 36767667
- PMCID: PMC9915322
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20032300
Randomized Controlled Trial Evaluating the Benefit of a Novel Clinical Decision Support System for the Management of COVID-19 Patients in Home Quarantine: A Study Protocol
Abstract
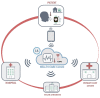
(1) Background: We present the protocol of a randomized controlled trial designed to evaluate the benefit of a novel clinical decision support system for the management of patients with COVID-19. (2) Methods: The study will recruit up to 500 participants (250 cases and 250 controls). Both groups will receive the conventional telephone follow-up protocol by primary care and will also be provided with access to a mobile application, in which they will be able to report their symptoms three times a day. In addition, patients in the active group will receive a wearable smartwatch and a pulse oximeter at home for real-time monitoring. The measured data will be visualized by primary care and emergency health service professionals, allowing them to detect in real time the progression and complications of the disease in order to promote early therapeutic interventions based on their clinical judgement. (3) Results: Ethical approval for this study was obtained from the Drug Research Ethics Committee of the Valladolid East Health Area (CASVE-NM-21-516). The results obtained from this study will form part of the thesis of two PhD students and will be disseminated through publication in a peer-reviewed journal. (4) Conclusions: The implementation of this telemonitoring system can be extrapolated to patients with other similar diseases, such as chronic diseases, with a high prevalence and need for close monitoring.
Keywords: Big Data; COVID-19; artificial intelligence; decision support system; mobile health; monitoring; telemedicine; wearable.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Virtualized clinical studies to assess the natural history and impact of gut microbiome modulation in non-hospitalized patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 a randomized, open-label, prospective study with a parallel group study evaluating the physiologic effects of KB109 on gut microbiota structure and function: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled study.Trials. 2021 Apr 2;22(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05157-0. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33810796 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence mobile health platform for early detection of COVID-19 in quarantine subjects using a wearable biosensor: protocol for a randomised controlled trial.BMJ Open. 2020 Jul 22;10(7):e038555. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-038555. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32699167 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Imatinib for Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Oct 28;21(1):897. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04819-9. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33115543 Free PMC article.
-
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (inactivated, Vero cell): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Apr 13;22(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05180-1. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33849629 Free PMC article.
-
Controlled, double-blind, randomized trial to assess the efficacy and safety of hydroxychloroquine chemoprophylaxis in SARS CoV2 infection in healthcare personnel in the hospital setting: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Jun 3;21(1):472. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04400-4. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32493494 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Randomized Controlled Trial to Assess the Feasibility of a Novel Clinical Decision Support System Based on the Automatic Generation of Alerts through Remote Patient Monitoring.J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 8;13(19):5974. doi: 10.3390/jcm13195974. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39408035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center. [(accessed on 25 November 2022)]. Available online: https://bit.ly/3whFNtc.
-
- Zhou F., Yu T., Du R., Fan G., Liu Y., Liu Z., Xiang J., Wang Y., Song B., Gu X., et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395:1054–1062. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical