Changes in Body Composition and Motor Fitness of Young Female Volleyball Players in an Annual Training Cycle
- PMID: 36767839
- PMCID: PMC9915199
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20032473
Changes in Body Composition and Motor Fitness of Young Female Volleyball Players in an Annual Training Cycle
Abstract
Background: Modern volleyball requires a high level of motor preparation, specific body build and optimal body composition.
Objectives: The aim of this study was to determine changes in body build, body composition and motor skills in young volleyball female players during an annual training cycle.
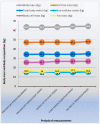
Methods: The research group was comprised of 36 female athletes aged 14-16 years, who were monitored throughout a whole season using a longitudinal study design. Body composition was estimated by bioelectrical impedance analysis. Motor fitness was assessed with the following tests: vertical jumping tests (based on one-handed and two-handed reach, standing vertical jump and running vertical jump), standing long jump and 2 kg medicine ball throw. Measurements were carried out at the beginning of the preparatory period, after its completion, in the middle of the start period, at the end of the start period and during transition periods.
Results: The study showed significant changes in body composition and motor fitness level during the annual training cycle. These changes differ in subsequent periods of the macrocycle. The most pronounced changes occurred after the preparatory period and concerned increases in fat-free mass, total water content and cell mass. A significant reduction in fat content was also noted at this point.
Conclusions: Systematic monitoring of morpho-functional changes in young female volleyball players over extended periods provides them a chance to maintain their optimal fitness level.
Keywords: body composition; motoric tests; periodization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Junior N.K.M. Specific periodization for the volleyball: The importance of the residual training effects. MOJ Sports Med. 2020;4:4–11. doi: 10.15406/mojsm.2020.04.00086. - DOI
-
- Bompa T.O., Haff G. Periodization: Theory and Methodology of Training. 5th ed. Human Kinetics; Champaign, IL, USA: 2009. pp. 123–186.
-
- Pastuszak A., Buśko K., Kalka E. Somatotype and body composition of volleyball players and untrained female students—Reference group for comparison in sport. Anthropol. Rev. 2016;79:461–470. doi: 10.1515/anre-2016-0033. - DOI
-
- Wnorowski K. Relations between technical-tactical competence and speed-force skills in women volleyball players. Res. Yearbook. 2007;13:226–229.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources