Overview of Sigma-1R Subcellular Specific Biological Functions and Role in Neuroprotection
- PMID: 36768299
- PMCID: PMC9916267
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24031971
Overview of Sigma-1R Subcellular Specific Biological Functions and Role in Neuroprotection
Abstract
For the past several years, fundamental research on Sigma-1R (S1R) protein has unveiled its necessity for maintaining proper cellular homeostasis through modulation of calcium and lipid exchange between the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondria, ER-stress response, and many other mechanisms. Most of these processes, such as ER-stress response and autophagy, have been associated with neuroprotective roles. In fact, improving these mechanisms using S1R agonists was beneficial in several brain disorders including neurodegenerative diseases. In this review, we will examine S1R subcellular localization and describe S1R-associated biological activity within these specific compartments, i.e., the Mitochondrion-Associated ER Membrane (MAM), ER-Lipid Droplet (ER-LD) interface, ER-Plasma Membreane (ER-PM) interface, and the Nuclear Envelope (NE). We also discussed how the dysregulation of these pathways contributes to neurodegenerative diseases, while highlighting the cellular mechanisms and key binding partners engaged in these processes.
Keywords: ER stress; Sigma-1R; calcium; chaperone; endoplasmic reticulum; homeostasis; lipid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




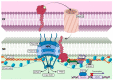
References
-
- Feigin V.L., Nichols E., Alam T., Bannick M.S., Beghi E., Blake N., Fischer F. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:459–480. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30499-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

