Immunopharmacological Activities of Luteolin in Chronic Diseases
- PMID: 36768462
- PMCID: PMC9917216
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24032136
Immunopharmacological Activities of Luteolin in Chronic Diseases
Abstract
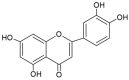
Flavonoids have been shown to have anti-oxidative effects, as well as other health benefits (e.g., anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor functions). Luteolin (3', 4', 5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone) is a flavonoid found in vegetables, fruits, flowers, and herbs, including celery, broccoli, green pepper, navel oranges, dandelion, peppermint, and rosemary. Luteolin has multiple useful effects, especially in regulating inflammation-related symptoms and diseases. In this paper, we summarize the studies about the immunopharmacological activity of luteolin on anti-inflammatory, anti-cardiovascular, anti-cancerous, and anti-neurodegenerative diseases published since 2018 and available in PubMed or Google Scholar. In this review, we also introduce some additional formulations of luteolin to improve its solubility and bioavailability.
Keywords: bioinformatics analysis; cancer; chronic disease; flavonoid; in vitro; in vivo; luteolin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
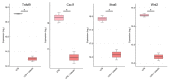

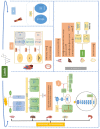
Similar articles
-
Luteolin as an anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective agent: A brief review.Brain Res Bull. 2015 Oct;119(Pt A):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2015.09.002. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Brain Res Bull. 2015. PMID: 26361743 Review.
-
Diabetes and its Complications: Role of Luteolin, A Wonder Chemical from the Natural Source.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024;21(1):e290224227537. doi: 10.2174/0115733998285798240217084632. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024. PMID: 38425118 Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of luteolin: A review of in vitro, in vivo, and in silico studies.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Oct 28;225:342-358. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.05.019. Epub 2018 May 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29801717 Review.
-
Distribution and biological activities of the flavonoid luteolin.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2009 Jan;9(1):31-59. doi: 10.2174/138955709787001712. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19149659 Review.
-
Luteolin, a flavonoid with potential for cancer prevention and therapy.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2008 Nov;8(7):634-46. doi: 10.2174/156800908786241050. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2008. PMID: 18991571 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitory Effect of Luteolin on Spike S1 Glycoprotein-Induced Inflammation in THP-1 Cells via the ER Stress-Inducing Calcium/CHOP/MAPK Pathway.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Oct 20;17(10):1402. doi: 10.3390/ph17101402. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459041 Free PMC article.
-
Dipsacus and Scabiosa Species-The Source of Specialized Metabolites with High Biological Relevance: A Review.Molecules. 2023 Apr 27;28(9):3754. doi: 10.3390/molecules28093754. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37175164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study on the regulatory mechanism of luteolin inhibiting WDR72 on the proliferation and metastasis of non small cell lung cancer.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 11;15(1):12398. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96666-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40216870 Free PMC article.
-
TRP Channel Inhibition and NF-κB Pathway Suppression in Human Ependymal Tumor cell-line by Achillea Biebersteinii Aqueous Extract.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Jul 31. doi: 10.1007/s12013-025-01852-w. Online ahead of print. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 40742507 No abstract available.
-
Role of post-translational modifications of Sp1 in cardiovascular diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Aug 26;12:1453901. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1453901. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39252788 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cook N.C., Samman S. Flavonoids—Chemistry, Metabolism, Cardioprotective Effects, and Dietary Sources. J. Nutr. Biochem. 1996;7:66–76. doi: 10.1016/0955-2863(95)00168-9. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

