Comparison of Tandem Mass Spectrometry and the Fluorometric Method-Parallel Phenylalanine Measurement on a Large Fresh Sample Series and Implications for Newborn Screening for Phenylketonuria
- PMID: 36768810
- PMCID: PMC9916910
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24032487
Comparison of Tandem Mass Spectrometry and the Fluorometric Method-Parallel Phenylalanine Measurement on a Large Fresh Sample Series and Implications for Newborn Screening for Phenylketonuria
Abstract
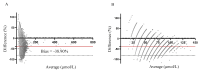
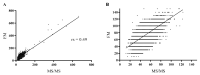
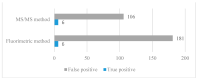
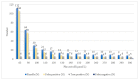
Phenylketonuria (PKU) was the first disease to be identified by the newborn screening (NBS) program. Currently, there are various methods for determining phenylalanine (Phe) values, with tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) being the most widely used method worldwide. We aimed to compare the MS/MS method with the fluorometric method (FM) for measuring Phe in the dried blood spot (DBS) and the efficacy of both methods in the NBS program. The FM was performed using a neonatal phenylalanine kit and a VICTOR2TM D fluorometer. The MS/MS method was performed using a NeoBaseTM 2 kit and a Waters Xevo TQD mass spectrometer. The Phe values measured with the MS/MS method were compared to those determined by the FM. The cut-off value for the NBS program was set at 120 µmol/L for FM and 85 µmol/L for MS/MS. We analyzed 54,934 DBS. The measured Phe values varied from 12 to 664 µmol/L, with a median of 46 µmol/L for the MS/MS method and from 10 to 710 µmol/L, with a median of 70 µmol/L for the FM. The Bland-Altman analysis indicated a bias of -38.9% (-23.61 µmol/L) with an SD of 21.3% (13.89 µmol/L) when comparing the MS/MS method to the FM. The Phe value exceeded the cut-off in 187 samples measured with FM and 112 samples measured with MS/MS. The FM had 181 false positives, while the MS/MS method had 106 false positives. Our study showed that the MS/MS method gives lower results compared to the FM. Despite that, none of the true positives would be missed, and the number of false-positive results would be significantly lower compared to the FM.
Keywords: comparison; false positive; fluorometric method (FM); newborn screening (NBS); phenylalanine (Phe); phenylketonuria (PKU); recall rate; tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Pourfarzam M., Zadhoush F. Newborn screening for inherited metabolic disorders; news and views. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2013;18:801–808.
-
- Repič Lampret B., Remec Ž.I., Drole Torkar A., Žerjav Tanšek M., Šmon A., Koračin V., Čuk V., Perko D., Ulaga B., Jelovšek A.M., et al. Expanded newborn screening program in Slovenia using tandem mass spectrometry and confirmatory next generation sequencing genetic testing. Zdr. Varst. 2020;95:256–263. doi: 10.2478/sjph-2020-0032. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grošelj U., Tanšek M.Ž., Podkrajšek K.T., Battelino T. Genetske in klinične značilnosti bolnikov s fenilketonurijo v Sloveniji. Zdr. Vestn. 2013;82:767–777.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

