The Role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metabolism
- PMID: 36768977
- PMCID: PMC9916527
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24032652
The Role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metabolism
Abstract
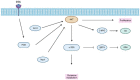
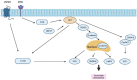
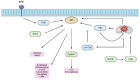
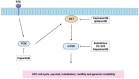
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths in the world. Metabolic reprogramming is considered a new hallmark of cancer, but it remains unclearly described in HCC. The dysregulation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway is common in HCC and is, therefore, a topic of further research and the concern of developing a novel target for liver cancer therapy. In this review, we illustrate mechanisms by which this signaling network is accountable for regulating HCC cellular metabolism, including glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism, amino acid metabolism, pyrimidine metabolism, and oxidative metabolism, and summarize the ongoing clinical trials based on the inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in HCC.
Keywords: HCC treatment; amino acid metabolism; cancer therapy; glucose metabolism; lipid metabolism; oxidative metabolism; pyrimidine metabolism; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Zheng Y.L., Li L., Jia Y.X., Zhang B.Z., Li J.C., Zhu Y.H., Li M.Q., He J.Z., Zeng T.T., Ban X.J., et al. LINC01554-Mediated Glucose Metabolism Reprogramming Suppresses Tumorigenicity in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Downregulating PKM2 Expression and Inhibiting Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Theranostics. 2019;9:796–810. doi: 10.7150/thno.28992. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

