Application of Antisense Conjugates for the Treatment of Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1
- PMID: 36769018
- PMCID: PMC9916419
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24032697
Application of Antisense Conjugates for the Treatment of Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1
Abstract
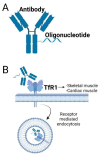
Myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) is one of the most common muscular dystrophies and can be potentially treated with antisense therapy decreasing mutant DMPK, targeting miRNAs or their binding sites or via a blocking mechanism for MBNL1 displacement from the repeats. Unconjugated antisense molecules are able to correct the disease phenotype in mouse models, but they show poor muscle penetration upon systemic delivery in DM1 patients. In order to overcome this challenge, research has focused on the improvement of the therapeutic window and biodistribution of antisense therapy using bioconjugation to lipids, cell penetrating peptides or antibodies. Antisense conjugates are able to induce the long-lasting correction of DM1 pathology at both molecular and functional levels and also efficiently penetrate hard-to-reach tissues such as cardiac muscle. Delivery to the CNS at clinically relevant levels remains challenging and the use of alternative administration routes may be necessary to ameliorate some of the symptoms experienced by DM1 patients. With several antisense therapies currently in clinical trials, the outlook for achieving a clinically approved treatment for patients has never looked more promising.
Keywords: antibody; bridged nucleic acids; cell-penetrating peptide; lipids; muscle; myotonic dystrophy; oligonucleotides; splicing.
Conflict of interest statement
MJAW and MAV are co-inventors of patents licensed to PepGen, a company dedicated to the peptide-based enhancement of delivery of therapeutic oligonucleotide analogs.
Figures
References
-
- Johnson N.E., Butterfield R.J., Mayne K., Newcomb T., Imburgia C., Dunn D., Duval B., Feldkamp M.L., Weiss R.B. Population-Based Prevalence of Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 Using Genetic Analysis of Statewide Blood Screening Program. Neurology. 2021;96:e1045–e1053. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000011425. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

