DNA Damage Response Mechanisms in Head and Neck Cancer: Significant Implications for Therapy and Survival
- PMID: 36769087
- PMCID: PMC9917521
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24032760
DNA Damage Response Mechanisms in Head and Neck Cancer: Significant Implications for Therapy and Survival
Abstract
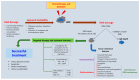
Head and neck cancer (HNC) is a term collectively used to describe a heterogeneous group of tumors that arise in the oral cavity, larynx, nasopharynx, oropharynx, and hypopharynx, and represents the sixth most common type of malignancy worldwide. Despite advances in multimodality treatment, the disease has a recurrence rate of around 50%, and the prognosis of metastatic patients remains poor. HNCs are characterized by a high degree of genomic instability, which involves a vicious circle of accumulating DNA damage, defective DNA damage repair (DDR), and replication stress. Nonetheless, the damage that is induced on tumor cells by chemo and radiotherapy relies on defective DDR processes for a successful response to treatment, and may play an important role in the development of novel and more effective therapies. This review summarizes the current knowledge on the genes and proteins that appear to be deregulated in DDR pathways, their implication in HNC pathogenesis, and the rationale behind targeting these genes and pathways for the development of new therapies. We give particular emphasis on the therapeutic targets that have shown promising results at the pre-clinical stage and on those that have so far been associated with a therapeutic advantage in the clinical setting.
Keywords: DNA damage response; genomic instability; head and neck cancer (HNC); head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC); homologous recombination (HR); non-homologous end joining (NHEJ).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration. Fitzmaurice C., Abate D., Abbasi N., Abbastabar H., Abd-Allah F., Abdel-Rahman O., Abdelalim A., Abdoli A., Abdollahpour I., et al. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-Years for 29 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5:1749–1768. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.2996. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

