PEDF Protects Endothelial Barrier Integrity during Acute Myocardial Infarction via 67LR
- PMID: 36769107
- PMCID: PMC9917376
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24032787
PEDF Protects Endothelial Barrier Integrity during Acute Myocardial Infarction via 67LR
Abstract
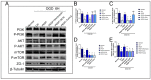
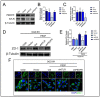
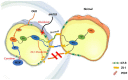
Maintaining the integrity and protecting the stability of tight junctions in endothelial cells is a potential therapeutic strategy against myocardial ischaemia. Laminin receptors (67LR) are highly expressed on endothelial cell membranes and are associated with endothelial barrier function. Herein, we sought to demonstrate the direct effects of pigment epithelial-derived factor (PEDF) on tight junctions between endothelial cells via 67LR during acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and elucidate its underlying mechanisms. We detected that PEDF directly increased the level of the tight junction protein zonula occludens protein 1 (ZO-1) after overexpression in vitro and in vivo using Western blotting. Evans Blue/TTC staining showed that PEDF significantly reduced the size of the infarcted myocardium. Immunofluorescence and the transwell cellular experiments suggested that PEDF significantly upregulated PI3K-AKT permeability and the distribution of ZO-1 between endothelial cells under OGD conditions. Interestingly, PEDF significantly upregulated the phosphorylation levels of PI3K-AKT-mTOR under oxygen and glucose deprivation conditions but had no significant effects on the total protein expression. The protective effect of PEDF on ZO-1 was significantly inhibited following the inhibition of PI3K-AKT-mTOR. The activation of phosphorylation of PI3K-AKT-mTOR by PEDF was blocked after silencing 67LR, as were the protective effects of PEDF on ZO-1. Therefore, we have reason to believe that PEDF increased ZO-1 expression through the 67LR-dependent PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway, thus maintaining tight junction stability and protecting cardiac function.
Keywords: 67LR; AMI; PEDF; ZO-1; endothelial cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Khera R., Secemsky E.A., Wang Y., Desai N.R., Krumholz H.M., Maddox T.M., Shunk K.A., Virani S.S., Bhatt D.L., Curtis J., et al. Revascularization Practices and Outcomes in Patients with Multivessel Coronary Artery Disease Who Presented With Acute Myocardial Infarction and Cardiogenic Shock in the US, 2009–2018. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020;180:1317–1327. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3276. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kushner F.G., Hand M., Smith S.C., Jr., King S.B., III, Anderson J.L., Antman E.M., Bailey S.R., Bates E.R., Blankenship J.C., Casey D.E., Jr., et al. 2009 focused updates: ACC/AHA guidelines for the management of patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (updating the 2004 guideline and 2007 focused update) and ACC/AHA/SCAI guidelines on percutaneous coronary intervention (updating the 2005 guideline and 2007 focused update): A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2009;120:2271–2306. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81870235/This work was supported by funds from the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- BE2019643/the Social Development Projects of Key R&D Programs in Jiangsu Province
- QNRC2016778/the Project of Invigorating Health Care through Science, Technology and Education, Jiangsu Provincial Medical Youth Talent
- KC21166/the Social Development Projects of Key R&D Programs in Xuzhou city (2022),the Social Development Projects of Medical and Health Programs in Xuzhou city
- KC21166/the Social Development Projects of Key R&D Programs in Xuzhou city (2022),the Social Development Projects of Medical and Health Programs in Xuzhou city
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

