Localisation of Intracellular Signals and Responses during Phagocytosis
- PMID: 36769146
- PMCID: PMC9917157
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24032825
Localisation of Intracellular Signals and Responses during Phagocytosis
Abstract
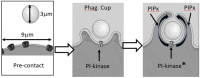
Phagocytosis is one of the most polarised of all cellular activities. Both the stimulus (the target for phagocytosis) and the response (its internalisation) are focussed at just one part of the cell. At the locus, and this locus alone, pseudopodia form a phagocytic cup around the particle, the cytoskeleton is rearranged, the plasma membrane is reorganised, and a new internal organelle, the phagosome, is formed. The effect of signals from the stimulus must, thus, both be complex and yet be restricted in space and time to enable an effective focussed response. While many aspects of phagocytosis are being uncovered, the mechanism for the restriction of signalling or the effects of signalling remains obscure. In this review, the details of the problem of restricting chemical intracellular signalling are presented, with a focus on diffusion into the cytosol and of signalling lipids along the plasma membrane. The possible ways in which simple diffusion is overcome so that the restriction of signalling and effective phagocytosis can be achieved are discussed in the light of recent advances in imaging, biophysics, and cell biochemistry which together are providing new insights into this area.
Keywords: Ca2+; cell signalling; cytoskeleton; neutrophils; phagocytosis; phospholipids.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Richards D.M. Receptor Models of Phagocytosis: The Effect of Target Shape. Adv. Expt. Med. Biol. 2020;1246:55–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

