Prunus Knotted-like Genes: Genome-Wide Analysis, Transcriptional Response to Cytokinin in Micropropagation, and Rootstock Transformation
- PMID: 36769369
- PMCID: PMC9918302
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24033046
Prunus Knotted-like Genes: Genome-Wide Analysis, Transcriptional Response to Cytokinin in Micropropagation, and Rootstock Transformation
Abstract
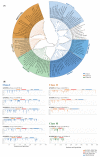
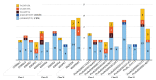
Knotted1-like homeobox (KNOX) transcription factors are involved in plant development, playing complex roles in aerial organs. As Prunus species include important fruit tree crops of Italy, an exhaustive investigation of KNOX genes was performed using genomic and RNA-seq meta-analyses. Micropropagation is an essential technology for rootstock multiplication; hence, we investigated KNOX transcriptional behavior upon increasing 6-benzylaminopurine (BA) doses and the effects on GF677 propagules. Moreover, gene function in Prunus spp. was assessed by Gisela 6 rootstock transformation using fluorescence and peach KNOX transgenes. Based on ten Prunus spp., KNOX proteins fit into I-II-M classes named after Arabidopsis. Gene number, class member distribution, and chromosome positions were maintained, and exceptions supported the diversification of Prunus from Cerasus subgenera, and that of Armeniaca from the other sections within Prunus. Cytokinin (CK) cis-elements occurred in peach and almond KNOX promoters, suggesting a BA regulatory role in GF677 shoot multiplication as confirmed by KNOX expression variation dependent on dose, time, and interaction. The tripled BA concentration exacerbated stress, altered CK perception genes, and modified KNOX transcriptions, which are proposed to concur in in vitro anomalies. Finally, Gisela 6 transformation efficiency varied (2.6-0.6%) with the genetic construct, with 35S:GFP being more stable than 35S:KNOPE1 lines, which showed leaf modification typical of KNOX overexpression.
Keywords: 6-benzyladenine; KNOX; Prunus spp.; bioinformatics; gene expression; genetic transformation; in vitro shoot multiplication; rootstocks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study or in the analyses of the data.
Figures







References
-
- Zhao M., Yang S., Chen C.Y., Li C., Shan W., Lu W., Cui Y., Liu X., Wu K. Arabidopsis BREVIPEDICELLUS interacts with the SWI2/SNF2 chromatin remodeling ATPase BRAHMA to regulate KNAT2 and KNAT6 expression in control of inflorescence architecture. PLoS Genet. 2015;11:e1005125. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005125. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

