Endovascular Treatment of Ruptured Blood Blister-like Aneurysms Using the LVIS EVO Stents
- PMID: 36769737
- PMCID: PMC9918215
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12031089
Endovascular Treatment of Ruptured Blood Blister-like Aneurysms Using the LVIS EVO Stents
Abstract
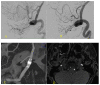
Blood blister-like aneurysms (BBAs) are rare cerebrovascular lesions that face serious challenges in surgical as well as endovascular treatment. In this paper, we present our experience in treating BBAs using the LVIS EVO stents. A total of 10 patients (mean age of 56.1 years) with 13 BBAs, who were admitted to our university hospital between April 2020 and November 2021 with a subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) due to aneurysm rupture, were treated using the LVIS EVO stents. Treatment of the BBAs consisted of stent-assisted coiling in four patients and stenting in six patients. The aneurysms were located within ICA (84.6%), VA (7.7%), and MCA (7.7%). Placement of the LVIS EVO stents was successful in all patients. No technical complications were observed. One in-stent thrombotic event occurred during the procedure. MRA for one-year follow-up was performed in nine patients. One patient died (Hunt and Hess Grade IV). LVIS EVO stents may be a beneficial treatment option for BBAs, as they provide high occlusion rates. However, the long-term efficacy remains uncertain.
Keywords: blood blister-like aneurysm; embolization; endovascular treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Rouchaud A., Brinjikji W., Cloft H., Kallmes D. Endovascular Treatment of Ruptured Blister-Like Aneurysms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis with Focus on Deconstructive versus Reconstructive and Flow-Diverter Treatments. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015;36:2331–2339. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4438. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

