One-Stage Immediate Alloplastic Breast Reconstruction in Large and Ptotic Breasts: An Institutional Algorithm
- PMID: 36769816
- PMCID: PMC9917996
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12031170
One-Stage Immediate Alloplastic Breast Reconstruction in Large and Ptotic Breasts: An Institutional Algorithm
Abstract
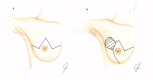
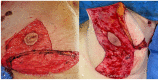
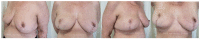
Immediate implant-based breast reconstruction in patients with large and ptotic breasts may be challenging due to skin redundancy. The use of a reduction mammoplasty pattern for the mastectomy skin excision has proven to be a reliable option for these patients as it allows for a better shape, projection, and symmetrization. This approach has been described in the literature for both one- and two-stage reconstruction with either sub- or pre-pectoral reconstruction with an acellular dermal matrix (ADM) or non-biological mesh. One-stage immediate breast reconstructions have a positive significant impact on patients' psychosocial well-being and quality of life. The purpose of this paper is to describe an institutional algorithm that allows one to perform one-stage implant-based breast reconstructions in patients with large and ptotic breasts.
Keywords: algorithm; breast hypertrophy; breast reconstruction; mammoplasty; mastectomy; post-bariatric; ptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Heneghan H.M., Prichard R.S., Lyons R., Regan P.J., Kelly J.L., Malone C., McLaughlin R., Sweeney K.J., Kerin M.J. Quality of Life after Immediate Breast Reconstruction and Skin-Sparing Mastectomy–A Comparison with Patients Undergoing Breast Conserving Surgery. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2011;37:937–943. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2011.08.126. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Elder E.E., Brandberg Y., Björklund T., Rylander R., Lagergren J., Jurell G., Wickman M., Sandelin K. Quality of Life and Patient Satisfaction in Breast Cancer Patients after Immediate Breast Reconstruction: A Prospective Study. Breast. 2005;14:201–208. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2004.10.008. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

