Design, Synthesis, Spectroscopic Inspection, DFT and Molecular Docking Study of Metal Chelates Incorporating Azo Dye Ligand for Biological Evaluation
- PMID: 36769903
- PMCID: PMC9917733
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16030897
Design, Synthesis, Spectroscopic Inspection, DFT and Molecular Docking Study of Metal Chelates Incorporating Azo Dye Ligand for Biological Evaluation
Abstract
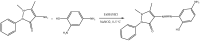
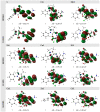
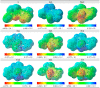
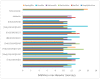
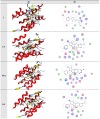
A new heterocyclic azo dye ligand (L) was synthesized by the combination of 4-amino antipyrine with 4-aminophenol. The new Cr(III), Mn(II), Fe(III), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), Zn(II), and Cd(II) complexes were synthesized in excellent yields. The metal chelate structures were elucidated using elemental analyses, FT-IR, 1H-NMR, mass, magnetic moment, diffused reflectance spectral and thermal analysis (TG-DTG), and molar conductivity measurement. According to the FT-IR study, the azo dye ligand exhibited neutral tri-dentate behavior, binding to the metal ions with the azo N, carbonyl O, and protonated phenolic OH. The 1H-NMR spectral study of the Zn(II) complex supported the coordination of the zo dye ligand without proton displacement of the phenolic OH. Diffused reflectance and magnetic moment studies revealed the octahedral geometry of the complexes, as well as their good electrolytic nature, excepting the Zn(II) and Cd(II) complexes, which were nonelectrolytes, as deduced from the molar conductivity study. The theoretical calculations of optimized HOMO-LUMO energies, geometrical parameters, electronic spectra, natural atomic charges, 3D-plots of MEP, and vibrational wavenumbers were computed and elucidated using LANL2DZ and 6-311G (d, p) basis sets of density functional theory (DFT) with the approach of B3LYP DFT and TD-DFT methods. The ligand and complexes have been assayed for their antimicrobial activity and compared with the standard drugs. Most of the complexes have manifested excellent antimicrobial activity against various microbial strains. A molecular docking investigation was also performed, to acquire more information about the binding mode and energy of the ligand and its metal complexes to the Escherichia coli receptor using molecular docking. Altogether, the newly created ligand and complexes showed positive antibacterial effects and are worth future study.
Keywords: antimicrobial activities; azo dye; complexes; docking; molecular geometries.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Spectroscopic study of molecular structures of novel Schiff base derived from o-phthaldehyde and 2-aminophenol and its coordination compounds together with their biological activity.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2009 Sep 1;73(5):833-40. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2009.04.005. Epub 2009 Apr 22. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2009. PMID: 19505840
-
Synthesis, structural elucidation, in vitro antibacterial activity, DFT calculations, and molecular docking aspects of mixed-ligand complexes of a novel oxime and phenylalanine.Bioorg Chem. 2022 Apr;121:105685. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.105685. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Bioorg Chem. 2022. PMID: 35231701
-
Biological activity studies on metal complexes of novel tridentate Schiff base ligand. Spectroscopic and thermal characterization.Eur J Med Chem. 2009 Dec;44(12):4801-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2009.07.028. Epub 2009 Aug 6. Eur J Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19758728
-
Development of New Azomethine Metal Chelates Derived from Isatin: DFT and Pharmaceutical Studies.Materials (Basel). 2022 Dec 22;16(1):83. doi: 10.3390/ma16010083. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36614421 Free PMC article.
-
Spectroscopic and Molecular Docking Studies of Cu(II), Ni(II), Co(II), and Mn(II) Complexes with Anticonvulsant Therapeutic Agent Gabapentin.Molecules. 2022 Jul 5;27(13):4311. doi: 10.3390/molecules27134311. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35807555 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
New Cation Sensors Based on Eugenol-Derived Azo Dyes.Molecules. 2025 Jun 28;30(13):2788. doi: 10.3390/molecules30132788. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40649303 Free PMC article.
-
Novel 2-Acetamido-2-ylidene-4-imidazole Derivatives (El-Saghier Reaction): Green Synthesis, Biological Assessment, and Molecular Docking.ACS Omega. 2023 Aug 9;8(33):30519-30531. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c03767. eCollection 2023 Aug 22. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37636903 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and in Silico Investigation of Organoselenium-Clubbed Schiff Bases as Potential Mpro Inhibitors for the SARS-CoV-2 Replication.Life (Basel). 2023 Mar 30;13(4):912. doi: 10.3390/life13040912. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37109441 Free PMC article.
-
Mitoxantrone and abacavir: An ALK protein-targeted in silico proposal for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.PLoS One. 2024 Feb 6;19(2):e0295966. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295966. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38319906 Free PMC article.
-
Azobenzene as Multi-Targeted Scaffold in Medicinal Chemistry.Molecules. 2024 Dec 12;29(24):5872. doi: 10.3390/molecules29245872. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39769961 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zollinger H. Color Chemistry. 2nd ed. VCH Weinheim; Weinheim, Germany: 1991.
-
- Ganesh R., Boardman G.D., Michelson D. Fate of azo dyes in sludges. Water Res. 1994;28:1367. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(94)90303-4. - DOI
-
- Abu-Dief A.M., El-Khatib R.M., Aljohani F.S., Al-Abdulkarim H.A., Alzahrani S., El-Sarrag G., Ismael M. Synthesis, structuralelucidation, DFT calculation, biological studies and DNA inter-action of some aryl hydrazone Cr3+, Fe3+, and Cu2+ chelates. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2022;97:107643. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2022.107643. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

