Microstructural Features and Microhardness of the Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Synthesized by Additive Plasma Wire Deposition Welding
- PMID: 36769947
- PMCID: PMC9917873
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16030941
Microstructural Features and Microhardness of the Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Synthesized by Additive Plasma Wire Deposition Welding
Abstract
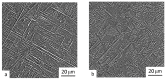
Wire arc additive manufacturing (AM) is able to replace the traditional manufacturing processes of Ti alloys. At the same time, the common drawback of Ti workpieces produced by AM via wire deposition welding is the formation of a coarse-grained dendritic structure, its strong anisotropy and, consequently, lower strength as compared to a monolithic alloy. In this work, a new method is proposed for the enhancement of the strength properties of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy synthesized by AM via wire deposition welding, which involves the use of a wire with an initial ultrafine-grained (UFG) structure. The UFG wire is characterized by a large number of defects of the crystalline lattice and grain boundaries, which will enable increasing the number of "crystallization centers" of the α-phase, leading to its refinement. The macro- and microstructure, phase composition and microhardness of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy samples were investigated. The microhardness of the alloy produced by layer-by-layer deposition welding using a UFG wire was shown to be on average 20% higher than that of the samples produced by a deposition welding using a conventional wire. The nature of this phenomenon is discussed, as well as the prospects of increasing the mechanical characteristics of Ti alloys produced by additive manufacturing.
Keywords: additive manufacturing; mechanical properties; microstructure; plasma wire deposition welding; titanium alloy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Boyer R., Welsch G., Collings E.W., editors. Materials Properties Handbook: Titanium Alloys. ASM International; Novelty, OH, USA: 1998.
-
- Lutjering G., Williams J.C. Titanium. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2007. New York, NY, USA.
-
- Williams D.F. Titanium for medical applications. In: Brunette D., Tengvall P., Textor M., Thomson P., editors. Titanium in Medicine. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2001. pp. 14–24.
-
- DebRoy T., Wei H.L., Zuback J.S., Mukherjee T., Elmer J.W., Milewski J.O., Beese A.M., Wilson-Heid A., De A., Zhang W. Additive manufacturing of metallic components—Process, structure and properties. Progr. Mater. Sci. 2018;92:112–2241. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2017.10.001. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

