Highly Washable and Conductive Cotton E-textiles Based on Electrochemically Exfoliated Graphene
- PMID: 36769966
- PMCID: PMC9917984
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16030958
Highly Washable and Conductive Cotton E-textiles Based on Electrochemically Exfoliated Graphene
Abstract
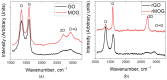
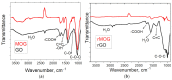
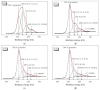
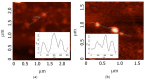
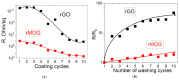
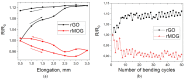
In this study, cotton e-textiles were obtained using two types of graphene oxide. The first type of graphene oxide was synthesized using the Hummers' method. The second type was obtained by the electrochemical exfoliation of graphite in an ammonium salt solution. It was shown that e-textiles based on electrochemically exfoliated graphene have a higher electrical conductivity (2 kΩ/sq) than e-textiles based on graphene oxide obtained by the Hummers' method (585 kΩ/sq). In addition, textiles based on electrochemically exfoliated graphene exhibit better washing and mechanical stress stability. The electrical resistance of the e-textiles increased only 1.86 times after 10 cycles of washing, compared with 48 times for the Hummers' method graphene oxide textiles. The X-ray photoelectron spectra of the two types of graphene oxides showed similarity in their functional compositions after reduction. Studies of individual graphene flakes by atomic force microscopy showed that graphene oxide of the second type had a smaller lateral size. Raman spectroscopy showed a higher degree of sp2 structure regeneration after reduction for the second type of graphene. These properties and the tendency to form agglomerated particles determine the mechanochemical stability and high electrical conductivity of e-textiles based on electrochemically exfoliated graphene.
Keywords: e-textiles; electrochemically exfoliated graphene; graphene; graphene oxide; wearable electronics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Electrical Properties of Textiles Treated with Graphene Oxide Suspension.Materials (Basel). 2021 Apr 16;14(8):1999. doi: 10.3390/ma14081999. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33923570 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Antimicrobial Properties of Graphene Oxide-Based Materials, Carbon Dots, and Their Combinations Deposited on Cotton Fabrics.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 14;25(10):5328. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105328. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791366 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating high electrical conductivity and photocatalytic activity in cotton fabric by cationizing for enriched coating of negatively charged graphene oxide.Carbohydr Polym. 2015 Oct 5;130:299-306. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.05.010. Epub 2015 May 19. Carbohydr Polym. 2015. PMID: 26076630
-
Antibacterial potential of electrochemically exfoliated graphene sheets.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017 Aug 15;500:30-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2017.03.110. Epub 2017 Apr 2. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017. PMID: 28395161
-
Synthesis and reduction of large sized graphene oxide sheets.Chem Soc Rev. 2017 Nov 27;46(23):7306-7316. doi: 10.1039/c7cs00485k. Chem Soc Rev. 2017. PMID: 29051935 Review.
References
-
- Choi W., Lahiri I., Seelaboyina R., Kang Y.S. Synthesis of graphene and its applications: A review. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2010;35:52–71. doi: 10.1080/10408430903505036. - DOI
-
- Zheng C., Zhang J., Zhang Q., You B., Chen G. Three dimensional Ni foam-supported graphene oxide for binder-free pseudocapacitor. Electrochim. Acta. 2015;152:216–221. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2014.11.132. - DOI
-
- Hu X., Huang T., Liu Z., Wang G., Chen D., Guo Q., Yang S., Jin Z., Lee J.-M., Ding G. Conductive graphene-based E-textile for highly sensitive, breathable, and water-resistant multimodal gesture-distinguishable sensors. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2020;8:14778–14787. doi: 10.1039/D0TA04915H. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

