Synergistic Inhibiting Effect of Phytochemicals in Rheum palmatum on Tyrosinase Based on Metabolomics and Isobologram Analyses
- PMID: 36770612
- PMCID: PMC9919157
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28030944
Synergistic Inhibiting Effect of Phytochemicals in Rheum palmatum on Tyrosinase Based on Metabolomics and Isobologram Analyses
Abstract
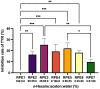
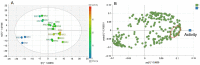
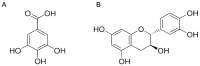
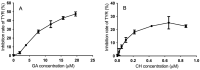
Tyrosinase (TYR) plays a key role in the enzymatic reaction that is responsible for a range of unwanted discoloration effects, such as food browning and skin hyperpigmentation. TYR inhibitors could, therefore, be candidates for skin care products that aim to repair pigmentation problems. In this study, we used a metabolomics approach combined with the isobologram analysis to identify anti-TYR compounds within natural resources, and evaluate their possible synergism with each other. Rheum palmatum was determined to be a model plant for observing the effect, of which seven extracts with diverse phytochemicals were prepared by way of pressurized solvent extraction. Each Rheum palmatum extract (RPE) was profiled using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and its activity of tyrosinase inhibition was evaluated. According to the orthogonal partial least square analysis used to correlate phytochemicals in RPE with the corresponding activity, the goodness of fit of the model (R2 = 0.838) and its predictive ability (Q2 = 0.711) were high. Gallic acid and catechin were identified as the active compounds most relevant to the anti-TYR effect of RPE. Subsequently, the activity of gallic acid and catechin were evaluated individually, and when combined in various ratios by using isobologram analysis. The results showed that gallic acid and catechin in the molar ratios of 9:5 and 9:1 exhibited a synergistic inhibition on TYR, with a combination index lower than 0.77, suggesting that certain combinations of these compounds may prove effective for use in cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and food industries.
Keywords: Rheum palmatum; catechin; gallic acid; isobologram analysis; metabolomics; orthogonal partial least square-modelling; synergistic effect; tyrosinase inhibitory activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Goldman A., Goldust M., Wollina U. Periorbital hyperpigmentation—Dark circles under the eyes; treatment suggestions and combining procedures. Cosmetics. 2021;8:26. doi: 10.3390/cosmetics8020026. - DOI
-
- Deng Y., Huang L., Zhang C., Xi P., Cheng J., Wang X., Liu L. Skin-care functions of peptides prepared from Chinese quince seed protein: Sequences analysis, tyrosinase inhibition and molecular docking study. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020;148:112331. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112331. - DOI
-
- Xie P., Huang L., Zhang C., Ding S., Deng Y., Wang X. Skin-care effects of dandelion leaf extract and stem extract: Antioxidant properties, tyrosinase inhibitory and molecular docking simulations. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018;111:238–246. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.10.017. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

