The Versatile Photo-Thermal Behaviour of a 2-Hydroxyazobenzene
- PMID: 36770849
- PMCID: PMC9920310
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28031183
The Versatile Photo-Thermal Behaviour of a 2-Hydroxyazobenzene
Abstract
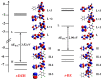
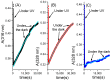
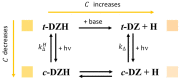
Photochromic compounds are employed in implementing neuron surrogates. They will boost the development of neuromorphic engineering in wetware. In this work, the photochromic behaviours of (E)-3,4,6-trichloro-2-(p-diazenil)-phenol (t-DZH) and its conjugated phenoxide base (t-DZ) have been investigated experimentally in three different media: (1) pure acetonitrile, (2) in water and acetonitrile mixed in a 1/1 volume ratio, and (3) in an aqueous micellar solution of 3-(N,N-Dimethylmyristylammonio)propanesulfonate (SB3-14). The analysis of the spectral and kinetic features of t-DZH and t-DZ has been supported by quantum-mechanical DFT calculations, the maximum entropy method, and the determination of their colourability (C). The versatility of t-DZH and t-DZ makes them promising molecular probes of micro-environments and potential ingredients of photochemical oscillators required for implementing pacemaker neurons capable of communicating through optical signals in wetware.
Keywords: azobenzene; molecular probe; molecular switch; photochemistry; photochromism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures






References
-
- Mitchell M. Artificial Intelligence. A Guide for Thinking Humans. 1st ed. Farrar, Straus and Giroux; New York, NY, USA: 2019.
-
- Zadeh L.A. Outline of a new approach to the analysis of complex systems and decision processes. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973;3:28–44. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.1973.5408575. - DOI
-
- Gentili P.L. Untangling Complex Systems: A Grand Challenge for Science. 1st ed. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2018. - DOI
-
- Indiveri G. Introducing Neuromorphic Computing and Engineering. Neuromorph. Comput. Eng. 2021;1:010401. doi: 10.1088/2634-4386/ac0a5b. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

