Biodiversity, Biochemical Profiling, and Pharmaco-Commercial Applications of Withania somnifera: A Review
- PMID: 36770874
- PMCID: PMC9921868
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28031208
Biodiversity, Biochemical Profiling, and Pharmaco-Commercial Applications of Withania somnifera: A Review
Abstract
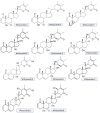
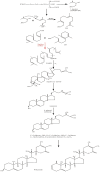
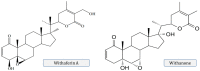
Withania somnifera L. Dunal (Ashwagandha), a key medicinal plant native to India, is used globally to manage various ailments. This review focuses on the traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, and pharmacological advances of its plant-derived constituents. It has been reported that at least 62 crucial and 48 inferior primary and secondary metabolites are present in the W. somnifera leaves, and 29 among these found in its roots and leaves are chiefly steroidal compounds, steroidal lactones, alkaloids, amino acids, etc. In addition, the whole shrub parts possess various medicinal activities such as anti-leukotriene, antineoplastic, analgesic, anti-oxidant, immunostimulatory, and rejuvenating properties, mainly observed by in vitro demonstration. However, the course of its medical use remains unknown. This review provides a comprehensive understanding of W. somnifera, which will be useful for mechanism studies and potential medical applications of W. somnifera, as well as for the development of a rational quality control system for W. somnifera as a therapeutic material in the future.
Keywords: Withania somnifera; ashwagandha; botany; pharmacological and biological activity; phytochemistry; traditional use.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- FAO 2005. [(accessed on 10 November 2021)]. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/a0050e/a0050e.pdf.
-
- Pushpgandhan P. Ethnobotany in India. Government of India; New Delhi, India: 1995. pp. 83–98. A Status Report.
-
- Prajapati N.D., Purohit S.S., Sharma A.K., Kumar T. A Handbook of Medicinal Plants—A Complete Source Book. Agrobios; Jodhpur, India: 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

