Anthocyanins: Potential Therapeutic Approaches towards Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
- PMID: 36770906
- PMCID: PMC9919338
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28031237
Anthocyanins: Potential Therapeutic Approaches towards Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
Abstract
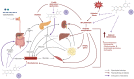
Overweight and obesity are present in about three-quarters of the adult population in Mexico. The inflammatory mechanisms subjacent to visceral white adipose tissue are accountable for the initiation and development of cardiometabolic alterations, including type 2 diabetes. Lifestyle changes are pillars within its therapeutics and, thus, current dietary modifications should include not only hypocaloric prescriptions with balanced macronutrient intake, preferably by increasing the amount of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, nuts and legumes, but in concomitance, bioactive substances, such as anthocyanins, have been correlated with lower incidence of this disease.
Keywords: anthocyanins; diabetes; functional foods; inflammation; phytochemicals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

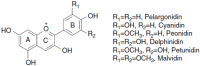

References
-
- Abubakar S.M., Ukeyima M.T., Spencer J.P.E., Lovegrove J.A. Acute Effects of Hibiscus Sabdariffa Calyces on Postprandial Blood Pressure, Vascular Function, Blood Lipids, Biomarkers of Insulin Resistance and Inflammation in Humans. Nutrients. 2019;11:341. doi: 10.3390/nu11020341. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arendt E.K., Zannini E. Cereal Grains for the Food and Beverage Industries. 1st ed. Elsevier; Berkeley, CA, USA: 2013.
-
- Castañeda-Ovando A., de Lourdes Pacheco-Hernández M., Páez-Hernández M.E., Rodríguez J.A., Galán-Vidal C.A. Chemical Studies of Anthocyanins: A Review. Food Chem. 2009;113:859–871. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.09.001. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

