Glutathione-Related Enzymes and Proteins: A Review
- PMID: 36771108
- PMCID: PMC9919958
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28031447
Glutathione-Related Enzymes and Proteins: A Review
Abstract
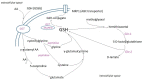
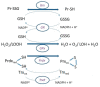
The tripeptide glutathione is found in all eukaryotic cells, and due to the compartmentalization of biochemical processes, its synthesis takes place exclusively in the cytosol. At the same time, its functions depend on its transport to/from organelles and interorgan transport, in which the liver plays a central role. Glutathione is determined as a marker of the redox state in many diseases, aging processes, and cell death resulting from its properties and reactivity. It also uses other enzymes and proteins, which enables it to engage and regulate various cell functions. This paper approximates the role of these systems in redox and detoxification reactions such as conjugation reactions of glutathione-S-transferases, glyoxylases, reduction of peroxides through thiol peroxidases (glutathione peroxidases, peroxiredoxins) and thiol-disulfide exchange reactions catalyzed by glutaredoxins.
Keywords: cell; glutathione; glutathione enzyme; glutathione system; glutathionylation; redox homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
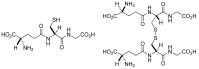
Similar articles
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Glutaredoxin Enzymes: Versatile Hubs for Thiol-Disulfide Exchange between Protein Thiols and Glutathione.J Mol Biol. 2019 Jan 18;431(2):158-177. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.12.006. Epub 2018 Dec 12. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30552876 Review.
-
The glutathione system and the related thiol network in Caenorhabditis elegans.Redox Biol. 2019 Jun;24:101171. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101171. Epub 2019 Mar 16. Redox Biol. 2019. PMID: 30901603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutaredoxin 2 catalyzes the reversible oxidation and glutathionylation of mitochondrial membrane thiol proteins: implications for mitochondrial redox regulation and antioxidant DEFENSE.J Biol Chem. 2004 Nov 12;279(46):47939-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408011200. Epub 2004 Aug 30. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15347644
-
Involvement of thiol-based mechanisms in plant development.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Aug;1850(8):1479-96. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.01.023. Epub 2015 Feb 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25676896 Review.
-
Nuclear thiol redox systems in plants.Plant Sci. 2016 Feb;243:84-95. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.12.002. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 26795153 Review.
Cited by
-
Disulfide stress and its role in cardiovascular diseases.Redox Biol. 2024 Sep;75:103297. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103297. Epub 2024 Aug 3. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 39127015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Influence of Oxidative Stress Markers in Patients with Ischemic Stroke.Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 6;14(9):1130. doi: 10.3390/biom14091130. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Update on Glutathione's Biosynthesis, Metabolism, Functions, and Medicinal Purposes.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(29):4579-4601. doi: 10.2174/0109298673251025230919105818. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37921175 Review.
-
The long-chain flavodoxin FldX1 improves the biodegradation of 4-hydroxyphenylacetate and 3-hydroxyphenylacetate and counteracts the oxidative stress associated to aromatic catabolism in Paraburkholderia xenovorans.Biol Res. 2024 Apr 1;57(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s40659-024-00491-4. Biol Res. 2024. PMID: 38561836 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating Nitric Oxide: Implications for Cytotoxicity and Cytoprotection.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Apr 23;13(5):504. doi: 10.3390/antiox13050504. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38790609 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hopkins F.G. On glutathione, a reinvestigation. J. Biol. Chem. 1929;84:269–320. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)77062-2. - DOI
-
- Hunter G., Eagles B.A. Glutathione. A critical study. J. Biol. Chem. 1927;72:147–166. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)84368-X. - DOI
-
- Simoni R.D., Hill R.L., Vaughan M. The discovery of glutathione by F. Gowland Hopkins and the beginning of biochemistry at Cambridge University. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:27–28. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(20)70350-9. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

