Microorganisms for Ginsenosides Biosynthesis: Recent Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives
- PMID: 36771109
- PMCID: PMC9921939
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28031437
Microorganisms for Ginsenosides Biosynthesis: Recent Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives
Abstract
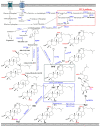
Ginsenosides are major bioactive compounds present in the Panax species. Ginsenosides exhibit various pharmaceutical properties, including anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antimetastatic, hypertension, and neurodegenerative disorder activities. Although several commercial products have been presented on the market, most of the current chemical processes have an unfriendly environment and a high cost of downstream processing. Compared to plant extraction, microbial production exhibits high efficiency, high selectivity, and saves time for the manufacturing of industrial products. To reach the full potential of the pharmaceutical resource of ginsenoside, a suitable microorganism has been developed as a novel approach. In this review, cell biological mechanisms in anticancer activities and the present state of research on the production of ginsenosides are summarized. Microbial hosts, including native endophytes and engineered microbes, have been used as novel and promising approaches. Furthermore, the present challenges and perspectives of using microbial hosts to produce ginsenosides have been discussed.
Keywords: Panax species; endophytes; engineered microorganisms; ginsenosides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Phytochemistry of ginsenosides: Recent advancements and emerging roles.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(5):613-640. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1952159. Epub 2021 Jul 19. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 34278879 Review.
-
Ginsenosides in cancer: A focus on the regulation of cell metabolism.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Dec;156:113756. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113756. Epub 2022 Oct 10. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 36228372 Review.
-
[Research progress on development and utilization of minor ginsenosides].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 Jan;49(2):304-314. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230824.201. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38403306 Chinese.
-
Progress on the Studies of the Key Enzymes of Ginsenoside Biosynthesis.Molecules. 2018 Mar 6;23(3):589. doi: 10.3390/molecules23030589. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29509695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biotransformation of ginsenosides by hydrolyzing the sugar moieties of ginsenosides using microbial glycosidases.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010 Jun;87(1):9-19. doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2567-6. Epub 2010 Apr 8. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20376631 Review.
Cited by
-
Plant-derived triterpenoid saponins: multifaceted roles and bioengineering prospects.Plant Cell Rep. 2025 Jul 8;44(8):172. doi: 10.1007/s00299-025-03483-0. Plant Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 40629160 Review.
-
Identification of genes involved in verazine biosynthesis in Veratrum grandiflorum and their heterologous production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jul 3;25(1):853. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06899-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40610854 Free PMC article.
-
Active Compounds of Panax ginseng in the Improvement of Alzheimer's Disease and Application of Spatial Metabolomics.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Dec 26;17(1):38. doi: 10.3390/ph17010038. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38256872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endophytic fungi of Panax sokpayensis produce bioactive ginsenoside Compound K in flask fermentation.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 23;14(1):9318. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56441-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38654024 Free PMC article.
-
Identify Regioselective Residues of Ginsenoside Hydrolases by Graph-Based Active Learning from Molecular Dynamics.Molecules. 2024 Jul 31;29(15):3614. doi: 10.3390/molecules29153614. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39125019 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

